Golf Sample
Turn-Based Framework integration
The Golf Sample uses several of the Turn-based Framework features, which are described in details on the next sections and briefly summarized below:
Each player has its own Turn Data instance to accumulate stats from the global current turn data.
Player's Turn Status is also kept updated by the Turn System.
When a Play/Skip Command Received signal is triggered by the framework, meaning that a valid Play/Skip Command has been received from the currently active player, respectively, the Play System strikes the ball performing physics related logic, and, in case is a Skip Command, the Turn System triggers a Turn Ended signal, so the turn is passed to another player;
Framework's Play Command Data wraps an FPVector3 and an FP used as ball striking direction and force, respectively, which is sent by the player via a Play Command;
When a Turn Ended signal is listened by the Turn System, it performs turn-related logic like activating another player's turn when a player skips or resolves a play, accumulating turn data stats on player's turn data instances and resetting global current turn fields.
It is also listened by Game End and Score Systems to check end game conditions and update score, respectively.
Game model
A game has a maximum number 2 of players through a constant used for initializing arrays and defining the maximum number of Ball entities.
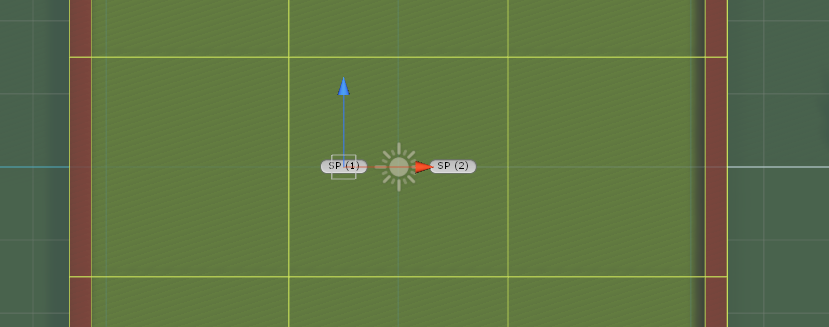
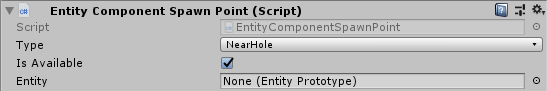
A Spawn Point is a struct to determine a spawn point's type, its position, if it's available and, if not, which entity has been spawned on it.
It can be of type Near Hole, which are spawn points used when Spawn Balls Near Hole is selected on Game Config asset; or of type Regular, for spawning balls on regular games.
A global array of spawn points data that is initialized on the Spawn System based on the data passed via the User Map asset instance.
When the game ends, a Gameplay Ended Event is raised in order to communicate it to Unity, so it can display a visual feedback.
It is raised by the Game End System when all end game conditions are met.
C#
#define MAX_PLAYERS 2
asset ConfigAssets;
asset GameConfig;
asset UserMap;
enum SpawnPointType { Regular, NearHole }
struct SpawnPoint
{
SpawnPointType Type;
Boolean IsAvailable;
FPVector3 Position;
entity_ref Entity;
}
global
{
array<SpawnPoint>[4] SpawnPoints;
}
synced event GameplayEnded { }
Ball model
The ball model is defined on the Ball.qtn file and is composed of the following fields:
- Actor: A component that holds a reference to the player that owns this entity.
The Actor activation state represents if a player is currently active on this game and it's used when loading a game from a saved file. - Turn Stats: An instance of a Turn Data struct to accumulate stats from the global Current Turn data.
Turn Status is also kept updated by the Turn System. - Last Position: Represents a ball's last position before being shot.
It's used for resetting a ball's position when landing on a Rough Field. - Has Completed Course: Represents if the player has completed current course by getting his ball to the course's hole.
It's checked and updated by the Play System. - End of Movement Timer: A timer that is increased by the Play System until a ball is considered as stopped, based on
- Score: Updated by the Score System when a players' Play Turn has ended.
If a player hasn't completed the course yet, it's 0.
Otherwise, it's the maximum number of strokes of the course +1, subtracted by the number of strokes the player needed to get the ball to the into the hole. - On Ball Shot Signal: Signal triggered when a ball is shot.
Used, for example, by the Turn System to set Turn Status to Resolving. - Input: Besides the Play Command sent by a player when striking a ball, a player sends input with current aiming direction and force bar mark position so other players can replicate the opponent's aiming on their side.
These values are meant just for visual feedback purposes and are not considered when the player actually strikes a ball, despite that in that case the Input and Play Command have the same aiming direction value.
C#
asset BallSpec;
component Actor
{
Boolean Active;
player_ref Player;
}
entity Ball[MAX_PLAYERS]
{
use Transform3D;
use DynamicBody3D;
use Prefab;
use Actor;
fields
{
TurnData TurnStats;
FPVector3 LastPosition;
Boolean HasCompletedCourse;
Int32 EndOfMovementTimer;
Int32 Score;
}
}
signal OnBallShot(Ball* b);
input
{
FPVector3 Direction;
FP ForceBarMarkPos;
}
Game Assets
Config Assets
A data asset that holds asset links to all other configuration assets of the game, like Game Config (see below) and Turn Config assets from the framework.
It's used to ease the process of initializing assets on Unity and serializing them on Quantum, also easing the process of adding new types and/or instances of data assets to the game.
On this sample, it's declared on the ConfigAssets.cs file:
C#
public partial class ConfigAssets
{
public GameConfigLink GameConfig;
public BallSpecLink BallSpec;
public TurnConfigLink StartCountdownConfig;
public TurnConfigLink PlayTurnConfig;
public TurnConfigLink CountdownTurnConfig;
}
It is initialized and serialized on RuntimeConfig.User.cs:
C#
partial class RuntimeConfig
{
public ConfigAssetsLink ConfigAssets;
partial void SerializeUserData(BitStream stream)
{
stream.Serialize(ref ConfigAssets.Guid);
}
}
On the Unity side, an instance of this data asset is initialized on Quantum Runner Local Debug for when playing on local debug mode:
And on UIRoom.cs script for when playing on online mode:
C#
RuntimeConfig config;
config.ConfigAssets.Guid = UnityDB.AllOf<ConfigAssetsAsset>().First().Settings.Guid;
To add a new custom data asset, add a link for it on the ConfigAssets.cs file, build the project and drag and drop the custom asset instance to a Config Assets instance on Unity.
Game Config
A data asset that holds values used on the simulation of the game in general:
- Spawn Balls Near Hole: Used by the Spawn System to determine if balls should be spawned on Regular or Near Hole spawn point types;
- Min-Max Strike Angle and Force: Min-max values used by the Play System for limiting a ball strike;
- Force Bar Velocity: Polled from Unity to update a force bar marking position when a player is aiming;
- Hit Hole Velocity Threshold: A velocity magnitude value below which the ball is considered as hitting a hole when triggering a hole collider;
- Hole Bump Force: A vertical force added to a ball when it hits a hole with a velocity magnitude higher than the "Hit Hole Velocity Threshold";
- Hole Trigger and Rough Field Layers: String fields for the physics layer names on Unity for the Hole Trigger and Rough Field, used by the Play System for detecting those layers when a balls hits a static collider.
C#
public partial class GameConfig {
public Boolean SpawnBallsNearHole;
public Int32 MinStrikeAngle;
public Int32 MaxStrikeAngle;
public Int32 MinStrikeForce;
public Int32 MaxStrikeForce;
public Int32 ForceBarVelocity;
public Int32 HitHoleVelocityThreshold;
public Int32 HoleBumpForce;
public string HoleTriggerLayer;
public string RoughFieldLayer;
}
User Map
A data asset that holds map specific data like the maximum number of strokes a player can have to finish a given course (map) that is used by the Game End System and Score System, and an array of map specific Spawn Points (check Game Model).
C#
public partial class UserMap
{
public Int32 MaxStrokes;
public SpawnPoint[] SpawnPoints;
}
Ball Spec
A data asset that holds ball related data:
- Radius: The sphere collider radius of the ball;
- Mass: The dynamic body mass of the ball;
- Physics Mat: A link to the ball's physics material;
- End of Movement Velocity Threshold: A velocity magnitude value above which the ball is still considered as moving;
- End of Movement Waiting in Ticks: How many ticks the Play System waits after the ball has stopped moving until it declares the end of the play;
- Player 1 Prefab Name: Name used for linking the 1st player's ball on simulation to it's prefab on Unity;
- Player 2 Prefab Name: Name used for linking the 2nd player's ball on simulation to it's prefab on Unity;
- Layer Name: The physics layer name of the ball.
C#
partial class BallSpec
{
public FP Radius;
public FP Mass;
public PhysicsMaterialLink PhysicsMat;
public FP EndOfMovementVelocityThreshold;
public Int32 EndOfMovementWaitingInTicks;
public string Player1PrefabName;
public string Player2PrefabName;
public string LayerName;
}
Golf Systems
Setup System
Handles initial ball setup when Player Data is received, like initializing Actor, Dynamic Body and Prefab components and also resetting player's Turn Data instances and spawning ball (check Spawn System below);
Also handles player data initialization when loading a previously saved game.
Is this case, player data doesn't need to be reset and the previous game data is mapped to the new player reference.
Spawn System
On initialization, reads map spawn points passed through User Map asset and assign them to the global Spawn Points array, then, when a ball's spawn is requested (check Setup System above), updates that ball's position to the first available spawn point, also considering if balls should be spawned near hole (Game Config) and the current spawn type, and then disables the spawn point.
Play System
Handles ball physics by striking the ball based on the Play Command data sent by the player and evaluates triggered collisions with the course's hole and with the outer Rough Field;
When a valid Play Command is received, the system clamps the strike data (direction and force) according to the values defined on the "Game Config asset", then strikes the ball applying a force to its Dynamic Body and triggers an "On Ball Shot signal";
If global current Turn status is Resolving, meaning that a ball is moving, the system checks every tick if its movement has ended, comparing its velocity magnitude to the threshold value defined on the Ball Spec asset.
If the velocity is below the threshold, an end-of-movement timer is increased until it reaches a waiting duration defined also on the Ball Spec, in which case the play is ended.
If a ball is triggering a Rough Field static collider (outer dark green field) when stopping, its position is reset to the one before the strike happened;

When a play ends, ball's Dynamic Body is disabled to avoid any unwanted interactions while that player's turn is Inactive.
The system then triggers a Turn Ended signal in order to communicate that to the Turn System;
When a ball triggers a static collider with "Hole" layer and its velocity is below a given threshold (Game Config asset), it's considered as hitting a hole and completing a course, in which case the play also ends.
Turn System
Handles turn related logic by using Turn-based Framework features.
When a ball is struck (check Play System above), resets active-player's and global-current-turn's statuses to Resolving;
When a valid Skip Command is received from active player, triggers a Turn Ended signal;
When a turn ends is triggered, checks the Turn Type: if it's a Countdown turn and there is an eligible ball for next turn, activates next ball's turn; if it's a Play turn, accumulates global current turn's stats on respective player's turn data, reset that player's status to Inactive and reset global current turn's Type to Countdown according to Countdown Turn Config on Config Assets.
Score System
When a Play turn ends, updates that turn active-ball's score according to the following rule: if the ball has completed the course (hit hole), its score is the maximum number of strokes allowed on the map + 1 (User Map asset), subtracted by number of strokes the player took to get the ball to the hole; otherwise, if the ball hasn't completed the course yet, its score is 0.
Game End System
When a turn ends, checks end game condition, which is true when all balls have taken the maximum number of strikes allowed on that map (User Map asset) or have completed the course (hit hole).
In that case, global current turn data is reset to default and a Gameplay Ended event is raised.
Unity
Camera
CameraController.cs handles main camera movement control.
It has a dummy transform, which is the position and rotation values the actual camera is always lerping towards, and a targeted entity, which is a game object with an Entity Prefab Root component that the camera is currently looking at, and is updated automatically when global current turn's entity is updated.
The controller reads player inputs to pan, tilt and zoom camera and has fields for:
- Relative Position: the position of the camera relative to the targeted entity;
- Relative Rotation: the amount of rotation added to the camera after it is positioned at relative position and is looking at targeted entity;
- Follow Target: determines if camera will follow targeted entity when it is moving;
- Lerp velocity: the step factor used when lerping the actual camera towards dummy transform;
- Zoom Sensitivity: scale factor used when zooming in and out on the targeted entity;
- Closest Distance: closest distance allowed when zooming in on the targeted entity;
- Farthest Distance: farthest distance allowed when zooming out on the targeted entity;
- Rotation Sensitivity: scale factor used when player is panning or tilting the camera;
- Invert Rotation: mouse drag values are inverted before panning or tilting the camera;
- Target clickable area radius: circle radius around targeted entity where it's considered as clicking on it.
Input
Input Manager
As a client machine can have multiple local players, Input Manager controls whom of these players has its inputs read and handled by other input scripts on each Unity frame Update.
It has C# static events for various input events, like mouse button events, which other scripts subscribe to.
Input Poller
Quantum simulation polls input from Unity at a given rate (check Input Send Rate on Deterministic Config).
InputPoller.cs is responsible for reading the most recently registered input for local players and sending injecting it into the simulation.
The input data is stored from the moment it is registered until it is overwritten by another input from that player, or that player's turn ends, in which case the registered input is reset to its default value.
This is useful because aiming data (check Aiming Display) is polled from simulation when the player who's aiming is remote, but polled from registered inputs on Input Poller when it's local, so the visual responsiveness is sharper.
Strike Input
StrikeInput.cs sends active player's aiming input for registration and polling on Input Poller.
The script listens to input events from active local player sent by the Input Manager and apply mouse dragging to update aiming direction, also constantly updating force bar marking position.
Strike Input has fields for:
- Aim Sensitivity: scale factor used when dragging the mouse and changing shooting direction;
- Reverse Controls: input drag values are inverted before applied to shooting direction;
- Clamp Direction: aiming direction angles are clamped, if necessary, according to Game Config asset min-max striking angle values (which are also double-checked on simulation) and maximum strike opening values (UI only, not clamped on simulation);
- Max Strike Opening Angle: Maximum opening angle relative to camera's facing direction when started aiming.
When a player is aiming and the mouse button is released, a Play Command is requested to be sent (check below) with current aim direction and force bar marking position.
Player Commands
CommandDispatcher.cs is used for sending all Play and Skip Commands requested by a given player to the simulation.
Player UI
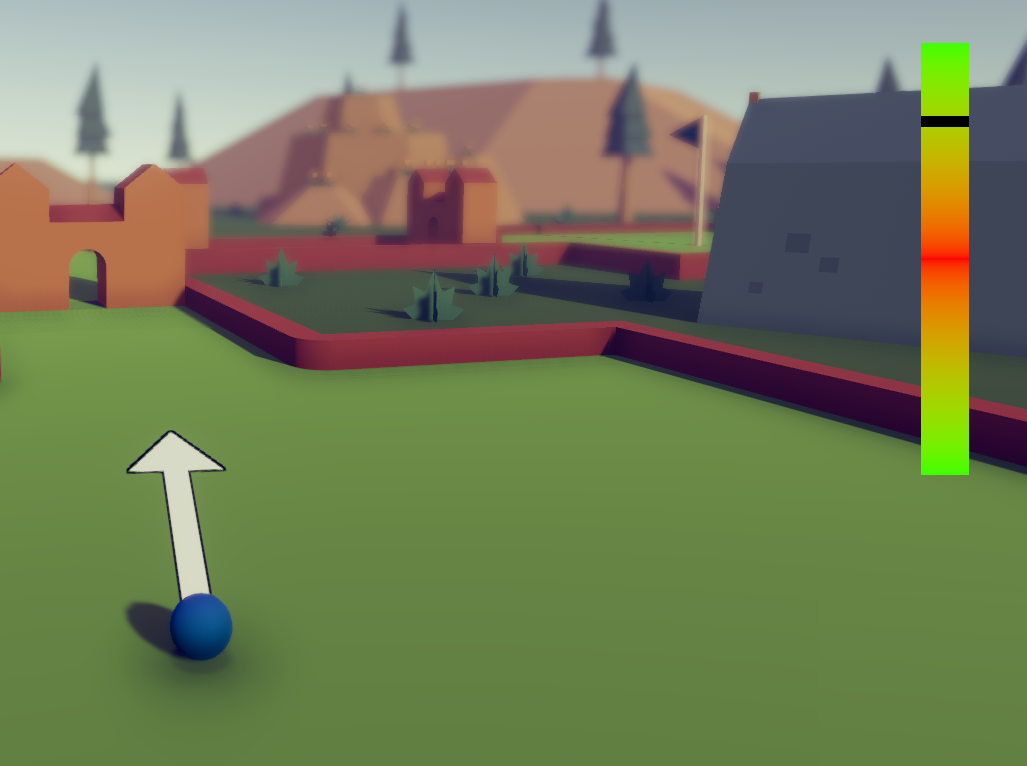
Aiming Display
AimingDisplay.cs is responsible for updating visual features (directional arrow and force bar) when a player is aiming.
When aiming player is local, it polls registered input for that player from Input Poller (check section above) for a sharper visual responsiveness, when aiming player is remote, polls most recent input from simulation for that player.
Turn Clock
UITurnClock.cs is responsible for polling global current turn's remaining turn duration from simulation when it's an Active turn that uses a timer and then updating displayed time on central clock panel.

Start Countdown
UIStartCountdown.cs is responsible for displaying a visual timer countdown at the centre of the screen before the first turn begins.
Player View
UIPlayerView.cs is responsible for polling turn data information for a given player and enabling/disabling/updating visual elements, like increasing turn number when a player's turn has ended; changing status text when player's status changes; making skip button non-interactable when turn is not active or player is not local and updating player's fillable ring timer.
Custom Interpolation
CustomInterpolation.cs overwrites an Entity Prefab Root position interpolation value with custom values for entities belonging to local and remote players.
Save Game
Save Game button persists current game state on a file that can be than loaded in another moment to continue a gameplay.
Default save file name is gamesave, but it can be changed by typing a file name on the given input field.
To load a previously saved game, type the file name (or leave it blank if the file was saved with its default name) when on Menu Scene, after entering into a room.

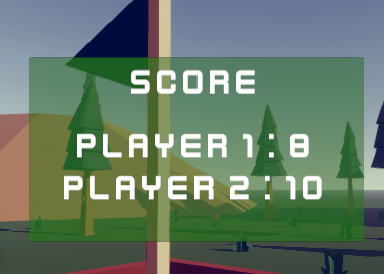
Score
UIScore.cs is responsible for enabling a score panel with players' score info when a Gameplay Ended event is raised by the simulation.
Spawn Points
Spawn Point components can be added to game objects in order to make them findable during the map baking process.
They can be of different types, which is translated from the game object component into the Spawn Point struct instance inside the simulation.
SpawnPointsBaker.cs implements a Map Data Baker Callback to read Spawn Points data from scene and add them to a User Map asset on current Map, that is sent to the simulation.