Architecture
This section describes relationship of the KCC to other components and communication flow.
Collider
- KCC collider is created at runtime as a child game object.
- Layer of the collider game object is controlled via
KCCSettings.ColliderLayerand is synchronized over network.
Rigidbody
Rigidbodycomponent is required byKCCand used for immediate position synchronization to the physics engine.Is Kinematicflag must be enabled (enforced at spawn).
Transform
- Transform component is used as write-only.
- Position and rotation is read only once during spawn.
Following diagram shows how KCC works from high-level perspective:
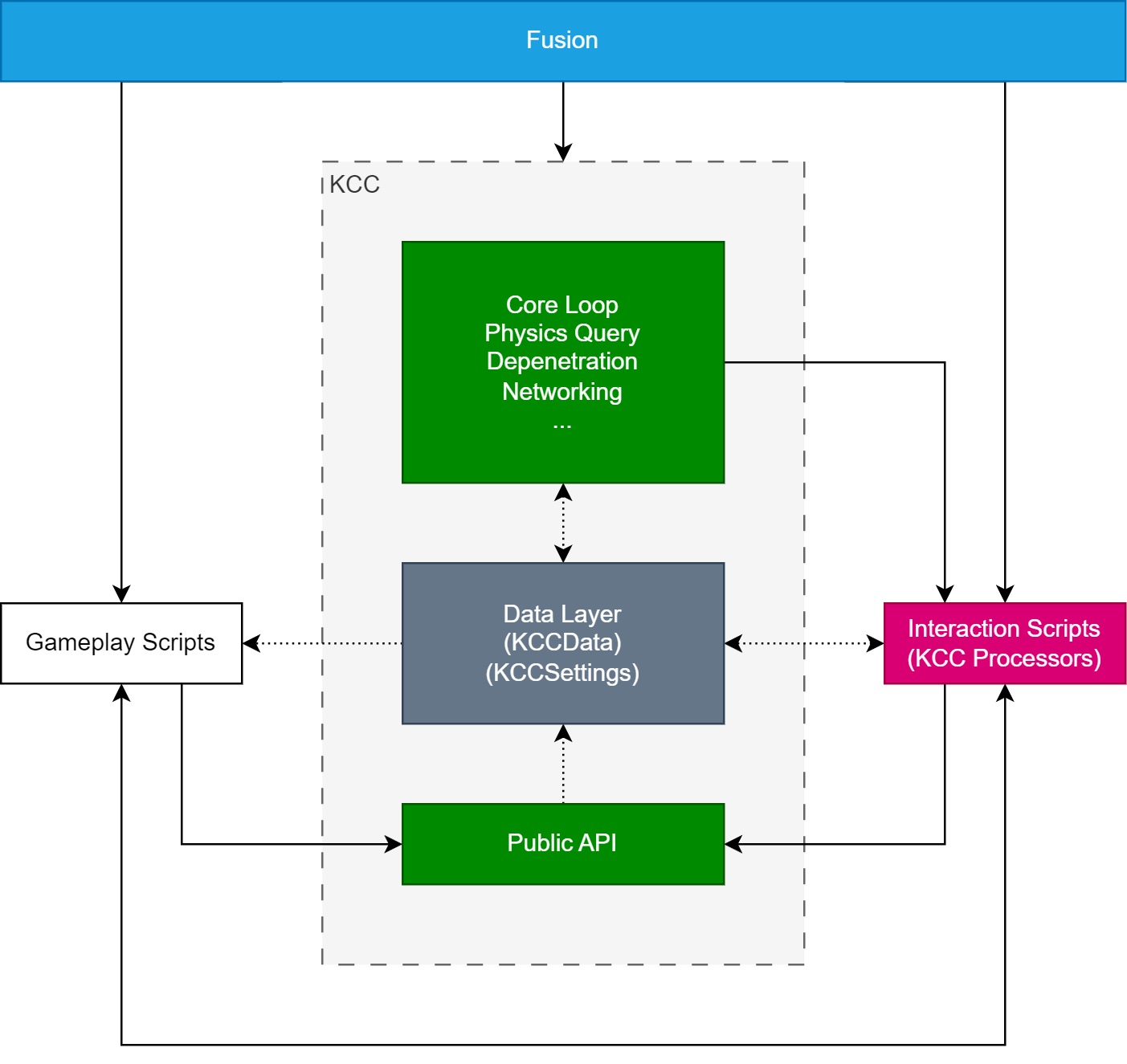
Gameplay Scripts
- User scripts which command KCC, representing “what to do” (move with a given direction, look at position, ignore a specific collider, do a jump, activate crouch, …).
- Read information from the Data Layer (for example
Is Grounded,Real Velocity, …). - Call Public API (
KCC.SetInputDirection(),KCC.SetLookRotation(),KCC.Jump()). - Can interoperate with Interaction Scripts.
- For example
Playerclass which translates input (mouse delta) to KCC actions (KCC.SetLookRotation()).
Interaction Scripts
- User scripts (implementing
IKCCProcessor), representing “how to move” (projecting input direction while grounded, 50% slower speed while crouching, calculating desired velocity). - The logic is injected indirectly during Core Loop execution.
- Write directly to the Data Layer or call Public API.
- Can interoperate with Gameplay Scripts.
- Can implement custom logic like any other
NetworkBehaviour. - For example
DashProcessorclass which force override KCC move velocity for 5 seconds upon activation.
Public API
- Provides set of commands which are immediately executed or transformed internally to be compatible with KCC execution flow, its features and current state (executing another set of commands, writing to Data Layer, safety checks).
- Abstracts complexity away from user.
- For example
KCC.SetRadius()which setsRadiusproperty inKCCSettingsand immediately propagate the values to collider.
Core Loop
- Handles base functionality like physics query, collision filtering, depenetration, networking, tracking colliders, step detection, ground snapping, networking, …
- Reads/writes from/to Data Layer.
- Executes stages to control movement via dependency injection (Interaction Scripts).
Following diagram shows a simplified application of above on a specific case:
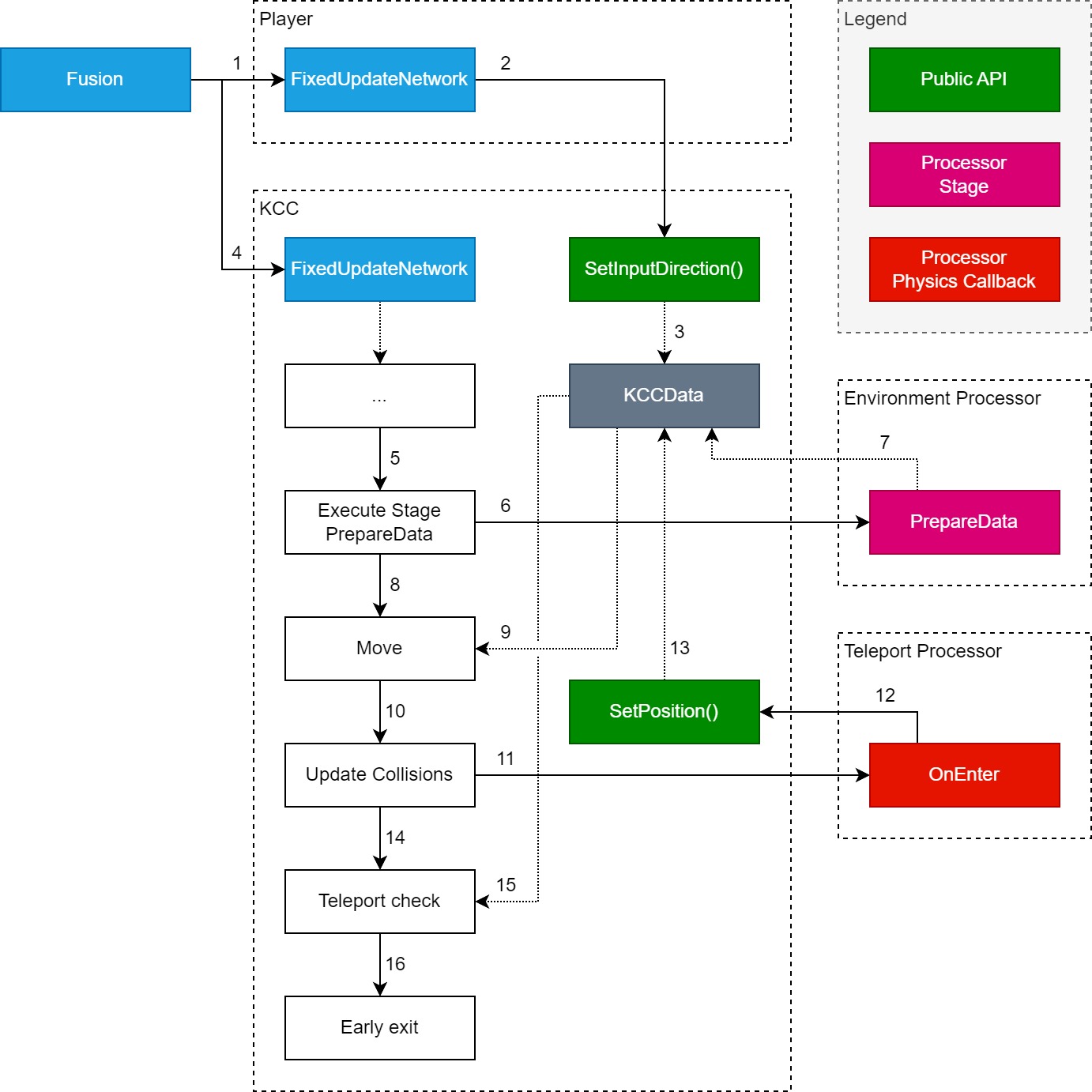
Player represents Gameplay Scripts. Environment Processor and Teleport Processor represent Interaction Scripts. Execution follows this order:
FixedUpdateNetwork()is called onPlayer- The
Playerscript callsKCC.SetInputDirection()with custom vector based on input from keyboard or joystick KCCwrites desired input direction intoKCCData.InputDirection(Data Layer)FixedUpdateNetwork()is called onKCCKCCexecutes series of commands up to a point where data for movement should be calculated by Interaction Scripts (KCC Processors)KCCexecutesPrepareDatastage on all processors that support this stage (in this caseEnvironment Processor)- The
Environment Processorinternally executes other set of stages which combine input direction and other properties and calculateKCCData.DynamicVelocityandKCCData.KinematicVelocityas a result - All stages are executed at this point,
KCCproceeds to actual move logic KCCcombines all calculated velocities and external delta into position delta candidateKCCmoves its collider by delta calculated in previous step, depenetrates overlapping colliders and refreshes internal list of collisionsKCCinvokesOnEnter()/OnExit()callbacks on newly entered/leaved colliders (in this caseTeleport Processor=>OnEnter())- The
Teleport ProcessorcallsKCC.SetPosition()with target position - The
KCC.SetPosition()immediately teleports theKCCto a given position and sets theKCCData.HasTeleportedflag to stop further execution (we don’t want to continue in movement after teleport) KCCresumes core loop after executing all callbacksKCCchecksKCCData.HasTeleportedflag for early exit (it is set to true in this case)KCCfinishes execution of current update (skipping remaining position delta)
As you may have guessed, the movement can be designed by using many different processors, each contributing/injecting its own logic. More info can be found in Interactions section.
Back to top