Disconnect & Reconnect
Overview
This sample project provides a few different strategies that can be used to handle players reconnecting to an online session after being disconnected. This sample contains code that works in both Shared and Client Host mode.
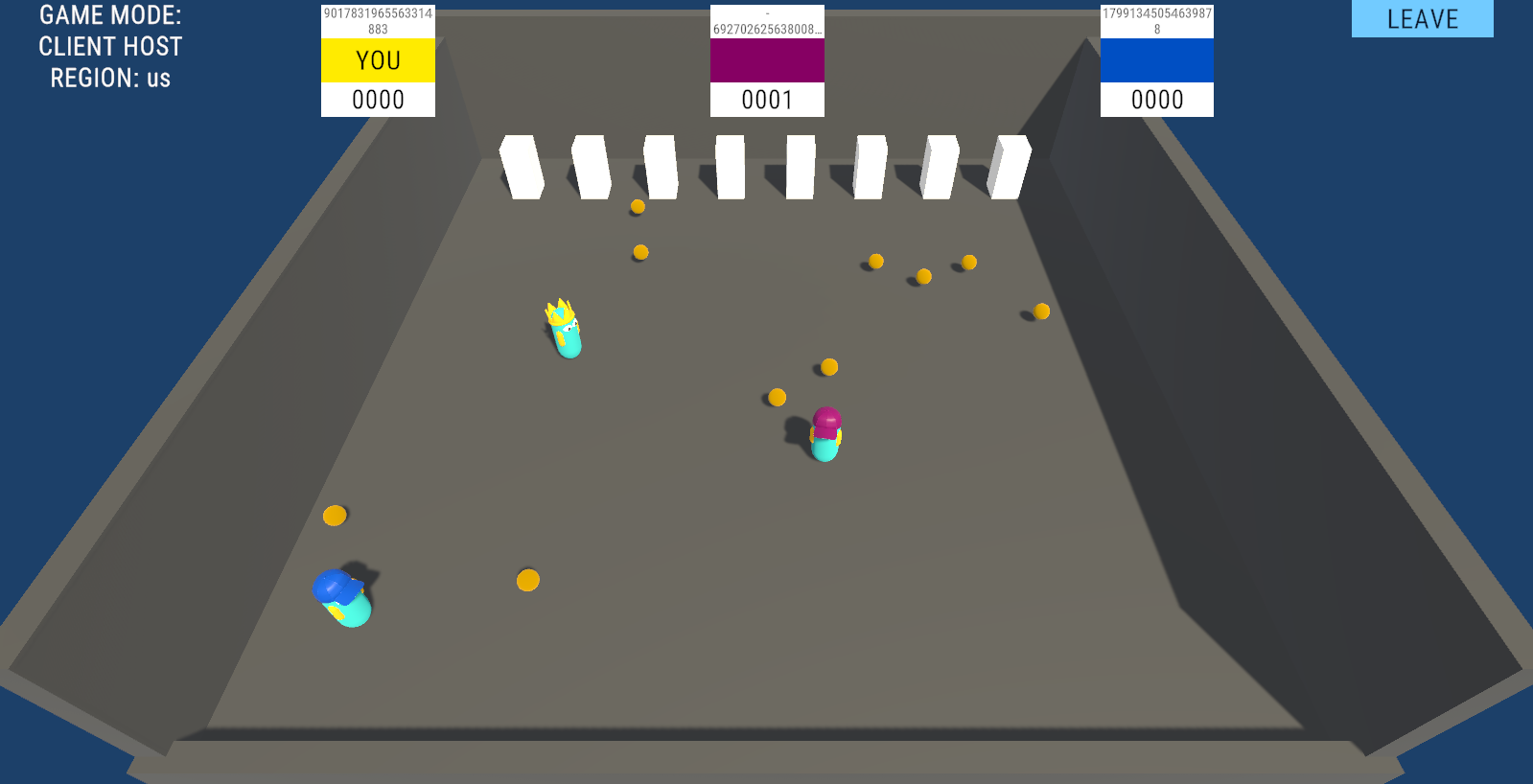
This sample is primarily focused on reconnection, so the gameplay is rather simple. Spawned players are represented by hat-wearing capsules. Left-clicking will direct the player towards that point. Colliding with yellow spheres will cause them to be collected and increase the player's score.
Download
| Version | Release Date | Download |
|---|---|---|
| 2.0.5 | 2月 27, 2025 | Disconnect Reconnect 2.0.5 |
Client Host Mode
In Client Host mode, there are a few features that can be used to help players reconnect to an existing session after disconnecting.
Connection Tokens
ConnectionTokens are a feature that can help players retake input authority of NetworkObjects they previously controlled when reconnecting to a session. A ConnectionToken is a byte array that can assigned as part of the StartGameArgs used when calling NetworkRunner.StartGame. During a session, this byte array can then be retrieved by calling NetworkRunner.GetPlayerConnectionToken(PlayerRef player).
In this sample, the ConnectionToken provided is a randomized long that is instantiated when the application starts. This value is converted to a byte array using SessionID and then provided to the StartGameArgs when starting a session through NetworkRunner.StartGame.
When a player joins, the Player Host keeps track of each NetworkObject that can be controlled by a player in a Dictionary<long, NetworkObject> where the keys are the ConnectionToken converted back to a long. If a reconnecting player provides the same ConnectionToken that they did previously, the Input Authority for the object will be reassigned to the reconnecting player instead of instantiating a new player.
Host Migration
ConnectionTokens work great when a Client disconnects; however, they are not sufficient for when the Player Host disconnects. In Client Host mode, the Player Host is the server, so when they disconnect, every Client is disconnected from the server, usually ending the session entirely. To address this, Host Migration is a feature that can be used to rebuild the session while assigning a new Client as the Player Host.
For Host Migration to trigger, the following must be done:
- A snapshot must be pushed. This can either be done by enabling
Enable Auto UpdateunderHost Migrationin theNetwork Project Config Assetor by manually callingNetworkRunner.PushHostMigrationSnapshot. - Assign an object that implements the
INetworkRunnerCallbacksinterface andINetworkRunnerCallbacks.OnHostMigrationto aNetworkRunnerusingNetworkRunner.AddCallbacks.
Implementing Host Migration
Host Migration implementation can be broken down into the following steps:
- Shutdown the current
NetworkRunner; it is recommending to provide the reason asShutdownReason.HostMigrationso whenINetworkRunnerCallbacks.OnShutdownis triggered, Clients can react differently. In this sample, for example, when aNetworkRunneris shutdown, theDisconnectWindowwill open; however, this will not happen if the reason for the shutdown isShutdownReason.HostMigration. - Unload the current scene; this is done so when the new version of the scene is loaded, the
NetworkObjectsthat were in the scene can be recreated. - Instantiate a new
NetworkRunnerand callNetworkRunner.StartGamewith newStartGameArgs. The two unique fields inStartGameArgsthat must be set are theHostMigrationToken, which contains information from the snapshots mentioned earlier, andHostMigrationResume, a method that will be called during the Host Migration process. - Recreate the
NetworkObjectsfrom the last snapshot that was pushed before Host Migration occurred by iterating throughNetworkRunner.GetResumeSnapshotNetworkObjects. - Copy the data for scene objects from the snapshot to those in the newly loaded scene by iterating through
NetworkRunner.GetResumeSnapshotNetworkSceneObjectsand then copying the state of the data of the old scene object to the new scene object by usingNetworkObject.CopyStateFrom.
The following code snippets demonstrates this process and can be found in GameController. This first snippet shows the implementation of INetworkRunnerCallbacks.OnHostMigration which uses asynchronous functionality.
C#
async void INetworkRunnerCallbacks.OnHostMigration(NetworkRunner runner, HostMigrationToken hostMigrationToken)
{
// Shutdown old Runner
await runner.Shutdown(shutdownReason: ShutdownReason.HostMigration);
// Unload the current game scene. If one is not found, we return to the main menu.
var completedLoad = new TaskCompletionSource<bool>();
var scene = SceneManager.GetSceneByName("GameScene");
if (!scene.IsValid())
{
ReturnToMainMenu();
return;
}
// We unload the game scene.
var unloadScene = SceneManager.UnloadSceneAsync(scene);
if (unloadScene != null) unloadScene.completed += (finishOp) => completedLoad.SetResult(true);
// A new runner is created
NetworkSceneInfo networkSceneInfo = default;
networkSceneInfo.AddSceneRef(SceneRef.FromIndex(1), LoadSceneMode.Additive, activeOnLoad: true);
// The host migration token will help resume the game and the host migration resume method is called once the host migration is ready
var startGameArgs = new StartGameArgs()
{
GameMode = hostMigrationToken.GameMode,
HostMigrationToken = hostMigrationToken,
HostMigrationResume = HostMigrationResume,
ConnectionToken = SessionID.ByteID,
Scene = networkSceneInfo,
};
// Create a new NetworkRunner
_instanceRunner = InstantiateRunner("GameRunner");
var result = await _instanceRunner.StartGame(startGameArgs);
if (result.Ok == false)
{
_instanceRunner = null;
}
else
{
var pushResult = await _instanceRunner.PushHostMigrationSnapshot();
}
}
The following code shows the implementation of GameController.HostMigrationResume:
C#
private void HostMigrationResume(NetworkRunner runnerMigration)
{
// Get a temporary reference for each NO from the old Host
foreach (var resumeNO in runnerMigration.GetResumeSnapshotNetworkObjects())
{
var hasTRSP = resumeNO.TryGetBehaviour<NetworkTRSP>(out var trsp);
var position = hasTRSP ? trsp.Data.Position : Vector3.zero;
var rotation = hasTRSP ? trsp.Data.Rotation : Quaternion.identity;
// Spawn a new object based on the previous objects
runnerMigration.Spawn(resumeNO, position: position, rotation: rotation, onBeforeSpawned: (networkRunner, newNO) =>
{
newNO.CopyStateFrom(resumeNO);
if (newNO.TryGetBehaviour<PlayerNetworkBehaviour>(out var playerBehaviour))
{
newNO.AssignInputAuthority(PlayerRef.None);
// Store mapping between Token and NetworkObject
_playersMap[playerBehaviour.Token] = newNO;
}
});
}
// Updates the state information of the scene objects loaded
foreach (var sceneObject in runnerMigration.GetResumeSnapshotNetworkSceneObjects())
{
sceneObject.Item1.CopyStateFrom(sceneObject.Item2);
if (sceneObject.Item1.TryGetBehaviour(out CollectableBehaviour sceneCollectable))
sceneCollectable.ForcePositionSync();
}
}
Note, since CollectableBehaviour.Spawned randomizes the position of these objects, CollectableBehaviour.ForcePositionSync during GameController.HostMigrationResume to set the previous NetworkTransform data back to the other.
For more information on Host Migration, the Host Migration Technical Sample can be referred to.
CloudConnectionLost Callback
Another feature that can handle disconnects and attempt a quick rejoin is the NetworkRunner.CloudConnectionLost callback. This callback provides
- The affected
NetworkRunner - The
ShutdownReason - A
boolthat signifies if a reconnection is being attempt.
This callback is provided to NetworkRunner.CloudConnectionLost. Refer to the Photon Connection Lost & Quick Reconnect documentation for more on this feature
Shared Mode
The three features previously mentioned only apply to Client Host mode. Though a ConnectionToken can be provided, NetworkRunner.GetPlayerConnectionToken(PlayerRef player) only works on the server or the Player Host and will return null otherwise. Host Migration also does not occur in Shared Mode because there is technically no Player Host; instead, the SharedModeMasterClient is transferred to another player if they disconnect, so Host Migration becomes unnecessary.
Reconnecting in Shared Mode
In Shared Mode, reconnecting cannot be done through the ConnectionToken system; however, the SessionID can still be used to try and reconnect a player who has rejoined with their previous avatar. To do this, the PlayerNetworkBehaviour prefab's Shared Mode Settings is set to Allow State Authority Override is set true and Destroy When State Authority Leaves is set to false. If this is done, the NetworkObject will not despawn when its State Authority leaves.
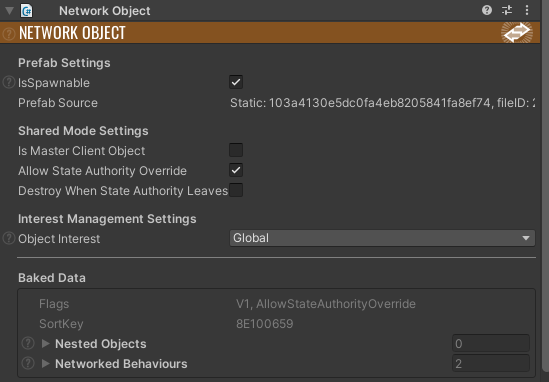
Then, inside GameController.OnPlayerJoined, before spawning a new player, all of the current PlayerNetworkBehaviour objects are iterated through, and if the value of their Token NetworkProperty matches the reconnecting player's SessionID, they will request State Authority of this object instead of spawning a new player. If they wait too long and the PlayerNetworkBehaviour has been despawned, a new one will be spawned.