Kinematic Character Controller (KCC)
簡介
運動學角色控制器(簡稱 KCC)用於根據自身一組規則在世界中移動角色。使用 KCC 而非基於物理 / 力的移動可以實現更精確的控制和靈敏的移動。儘管這些概念是每個遊戲的核心,但它們的定義差異很大,因為它們與整體遊戲玩法相關。因此,Quantum SDK 中包含的 KCC 應被視為一個起點;然而,遊戲開發者可能需要創建自己的 KCC,以獲得特定場景下的最佳結果。
Quantum 附帶兩個預建的 KCC,一個用於 2D(橫向滾動),一個用於 3D 移動。該 API 允許角色穿過地形、爬臺階、沿斜坡滑動和使用移動平臺。
KCC 在計算移動向量時會考慮靜態和動態物體的物理數據。物體會阻擋並定義角色的移動。與環境物體的碰撞回調也會被觸發。
重要提示: Quantum 還有一個 3D KCC 附加組件,它比預建組件更完整,並且在查詢時使用膠囊體形狀而非球形狀。它還具有非常靈活的處理器架構,有助於創建定義 KCC 邏輯的自定義方式,以適應遊戲的特定需求。
對於需要 3D KCC 的項目,我們的建議是使用附加組件而非預建組件。在此處了解更多信息:按此。
要求
要向實體添加 KCC 或使用 KCC,實體必須已經具有Transform組件。可以使用PhysicsBody,但 不是 必需的;通常不建議將PhysicsBody與 KCC 一起使用,因為物理系統可能會影響它,並導致意外移動。
有關 Quantum 物理學的一般信息,請先查看Physics文檔。
射線檢測與形狀重疊
KCC 僅使用形狀重疊(2D 為圓形,3D 為球形)來計算其移動。因此,僅具有 KCC 組件的實體將被射線檢測忽略。
如果實體需要進行射線檢測,則它還必須攜帶PhysicsCollider。
注意
本頁涵蓋 2D 和 3D KCC。
角色控制器組件
通過以下任一方式將 CharacterController 組件添加到實體:
- 在 Unity 中的實體原型上添加「Character Controller」組件;或者,
- 通過代碼添加「Character Controller」組件。
要通過代碼添加角色控制器,請參考以下示例。
C#
// 2D KCC
var kccConfig = frame.FindAsset<CharacterController2DConfig>(KCC_CONFIG_PATH);
var kcc = new CharacterController2D();
kcc.Init(frame, kccConfig)
f.Add(entity, kcc);
// 3D KCC
var kccConfig = frame.FindAsset<CharacterController3DConfig>(KCC_CONFIG_PATH);
var kcc = new CharacterController3D();
kcc.Init(frame, kccConfig)
f.Add(entity, kcc);
注意
組件創建後必須初始化。可用的初始化選項如下:
- (代碼)沒有 參數的
Init()方法,它將從Assets/Resources/DB/Configs加載DefaultCharacterController。 - (代碼)有 參數的
Init()方法,它將加載傳入的CharacterControllerConfig。 - (編輯器)將
CharacterControllerConfig添加到Character Controller組件的Config插槽中。
角色控制器配置
通過上下文菜單Create > Quantum > Assets > Physics > CharacterController2D/3D創建 KCC 配置資產。
默認配置資產
默認的 2D 和 3D KCC 配置資產位於Assets/QuantumUser/Resources/文件夾中。以下是 3D KCC 配置的樣子:
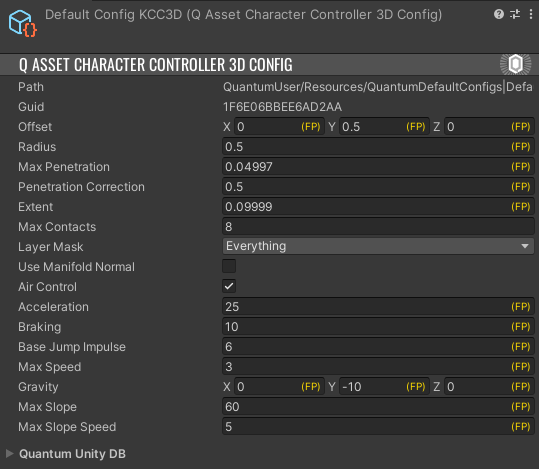
配置字段的簡要說明
- 偏移量 用於根據實體位置定義 KCC 的本地位置。它通常用於將 KCC 的中心定位在角色的腳部。請記住:KCC 用於移動角色,因此它不一定必須包裹角色的整個身體。
- 半徑 定義角色的邊界,應包含角色的水平大小。這用於判斷角色是否可以向特定方向移動、牆壁是否阻擋移動、是否要爬臺階或沿斜坡滑動。
- 最大穿透度 用於在角色穿透其他物理對象時使移動平滑。如果角色超過最大穿透度,將應用硬性修復並將其快速調整到正確位置。將此值減小到零將完全且立即應用所有修正;這可能導致移動不流暢。
- 範圍 定義預先檢測碰撞的半徑。
- 最大接觸點 用於選擇 KCC 計算的接觸點數量。1 通常運行良好,是性能最佳的選項。當遇到抖動的移動時,嘗試將其設置為 2;額外的開銷可以忽略不計。
- 圖層遮罩 定義 KCC 執行的物理查詢應考慮哪些碰撞器圖層。
- 空中控制 切換為
True,KCC 在不接觸地面時能夠進行移動調整。 - 加速度 定義角色加速的速度。
- 基礎跳躍衝量 定義調用 KCC
Jump()方法時的衝量力。如果沒有向該方法傳遞值,將使用此值。 - 最大速度 限制角色的最大水平速度。
- 重力 向 KCC 應用重力。
- 最大斜坡角度 定義角色可以上下行走的最大角度(以度為單位)。
- 最大斜坡速度 當移動類型為斜坡下落而非水平下落時,限制角色沿斜坡下滑的速度。
角色控制器 API
下面顯示的 API 側重於 3D KCC。2D 和 3D API 非常相似。
屬性和字段
每個 CharacterController 組件都有這些字段。
C#
public FP MaxSpeed { get; set;}
public FPVector3 Velocity { get; set;}
public bool Grounded { get; set;}
public AssetRef Config { get;}
提示
MaxSpeed是初始化後的緩存值。因此可以在運行時修改,例如在執行突刺時。
API
每個 KCC 組件都有以下方法:
C#
// Initialization
public void Init(FrameBase frame, CharacterController3DConfig config = null);
// Jump
public void Jump(FrameBase frame, bool ignoreGrounded = false, FP? impulse = null);
// Move
public void Move(FrameBase frame, EntityRef entity, FPVector3 direction, IKCCCallbacks3D callback = null, int? layerMask = null, Boolean? useManifoldNormal = null, FP? deltaTime = null);
// Raw Information
public static CharacterController3DMovement ComputeRawMovement(Frame frame, EntityRef entity, Transform3D* transform, CharacterController3D* kcc, FPVector3 direction, IKCCCallbacks3D callback = null, int? layerMask = null, bool? useManifoldNormal = null);
Jump和Move方法便於原型開發,而ComputeRawMovement提供創建自定義移動的關鍵信息。在 Quantum 提供的示例 KCC 中,ComputeRawMovement的信息被內部控制方法ComputeRawSteer用於計算Move中使用的控制。
重要提示:
下面介紹Jump(), Move()和ComputeRawSteer()的實現,以幫助理解並創建特定於遊戲需求的自定義實現。
CharacterController3DMovement
ComputeRawMovement()通過執行形狀重疊和處理數據來計算控制所需的環境數據。該方法返回一個CharacterController3DMovement結構,然後可以應用於角色移動。所提供的移動數據也可用於創建自定義控制實現。
CharacterController3DMovement結構包含以下信息:
C#
public enum CharacterMovementType
{
None, // grounded with no desired direction passed
FreeFall, // no contacts within the Radius
SlopeFall, // there is at least 1 ground contact within the Radius, specifically a contact with a normal angle vs -gravity <= maxSlopeAngle). It is possible to be "grounded" without this type of contact (see Grounded property in the CharacterController3DMovement)
Horizontal, // there is NO ground contact, but there is at least one lateral contact (normal angle vs -gravity > maxSlopeAngle)
}
public struct CharacterController3DMovement
{
public CharacterMovementType Type;
// the surface normal of the closest unique contact
public FPVector3 NearestNormal;
// the average normal from all contacts
public FPVector3 AvgNormal;
// the normal of the closest contact that qualifies as ground
public FPVector3 GroundNormal;
// the surface tangent (from GroundNormal and the derived direction) for Horizontal move, or the normalized desired direction when in CharacterMovementType.FreeFall
public FPVector3 Tangent;
// surface tangent computed from closest the contact normal vs -gravity (does not consider current velocity of CC itself).
public FPVector3 SlopeTangent;
// accumulated projected correction from all contacts within the Radius. It compensates with dot-products to NOT overshoot.
public FPVector3 Correction;
// max penetration of the closest contact within the Radius
public FP Penetration;
// uses the EXTENDED radius to assign this Boolean AND the GroundedNormalas to avoid oscilations of the grounded state when moving over slightly irregular terrain
public Boolean Grounded;
// number of contacts within Radius
public int Contacts;
}
ComputeRawMovement()被Move()方法使用。
Jump()
Jump只是向 KCC 的當前速度添加一個衝量,並切換 Jumped 布林值,該值將由內部ComputeRawSteer方法處理。
C#
public void Jump(FrameBase frame, bool ignoreGrounded = false, FP? impulse = null) {
if (Grounded || ignoreGrounded) {
Velocity.Y.RawValue = impulse?.RawValue ?? frame.FindAsset<CharacterController3DConfig>(Config.Id).BaseJumpImpulse.RawValue;
Jumped = true;
}
}
Move()
Move()在計算角色的新位置時考慮以下因素:
- 當前位置
- 方向
- 重力
- 跳躍
- 斜坡
- 更多
所有這些方面都可以在傳遞給Init()方法的配置資產中定義。這便於開發具有地形、網格碰撞器和基本體的 FPS/TPS/ 動作遊戲原型。
注意: 由於它計算所有內容並返回最終的FPVector3結果,因此它對移動本身沒有太多控制。要更嚴格地控制移動,請使用ComputeRawMovement()並創建自定義控制 + 移動。
C#
public void Move(Frame frame, EntityRef entity, FPVector3 direction, IKCCCallbacks3D callback = null, int? layerMask = null, Boolean? useManifoldNormal = null, FP? deltaTime = null) {
Assert.Check(frame.Has<Transform3D>(entity));
var transform = frame.GetPointer<Transform3D>(entity);
var dt = deltaTime ?? frame.DeltaTime;
CharacterController3DMovement movementPack;
fixed (CharacterController3D* thisKcc = &this) {
movementPack = ComputeRawMovement(frame, entity, transform, thisKcc, direction, callback, layerMask, useManifoldNormal);
}
ComputeRawSteer(frame, ref movementPack, dt);
var movement = Velocity * dt;
if (movementPack.Penetration > FP.EN3) {
var config = frame.FindAsset<CharacterController3DConfig>(Config.Id);
if (movementPack.Penetration > config.MaxPenetration) {
movement += movementPack.Correction;
} else {
movement += movementPack.Correction * config.PenetrationCorrection;
}
}
transform->Position += movement;
}
ComputeRawSteer()
控制包括根據角色的位置、半徑和速度計算移動,並在必要時糾正移動。
ComputeRawSteer是一個內部方法,它根據角色當前執行的移動類型進行大部分移動計算。在示例 KCC 中,Move從ComputeRawMovement請求movementPack值,並將它們傳遞給ComputeRawSteer。
C#
private void ComputeRawSteer(FrameThreadSafe f, ref CharacterController3DMovement movementPack, FP dt) {
Grounded = movementPack.Grounded;
var config = f.FindAsset(Config);
var minYSpeed = -FP._100;
var maxYSpeed = FP._100;
switch (movementPack.Type) {
// FreeFall
case CharacterMovementType.FreeFall:
Velocity.Y -= config._gravityStrength * dt;
if (!config.AirControl || movementPack.Tangent == default(FPVector3)) {
Velocity.X = FPMath.Lerp(Velocity.X, FP._0, dt * config.Braking);
Velocity.Z = FPMath.Lerp(Velocity.Z, FP._0, dt * config.Braking);
} else {
Velocity += movementPack.Tangent * config.Acceleration * dt;
}
break;
// Grounded movement
case CharacterMovementType.Horizontal:
// apply tangent velocity
Velocity += movementPack.Tangent * config.Acceleration * dt;
var tangentSpeed = FPVector3.Dot(Velocity, movementPack.Tangent);
// lerp current velocity to tangent
var tangentVel = tangentSpeed * movementPack.Tangent;
var lerp = config.Braking * dt;
Velocity.X = FPMath.Lerp(Velocity.X, tangentVel.X, lerp);
Velocity.Z = FPMath.Lerp(Velocity.Z, tangentVel.Z, lerp);
// we only lerp the vertical velocity if the character is not jumping in this exact frame,
// otherwise it will jump with a lower impulse
if (Jumped == false) {
Velocity.Y = FPMath.Lerp(Velocity.Y, tangentVel.Y, lerp);
}
// clamp tangent velocity with max speed
var tangentSpeedAbs = FPMath.Abs(tangentSpeed);
if (tangentSpeedAbs > MaxSpeed) {
Velocity -= FPMath.Sign(tangentSpeed) * movementPack.Tangent * (tangentSpeedAbs - MaxSpeed);
}
break;
// Sliding due to excessively steep slope
case CharacterMovementType.SlopeFall:
Velocity += movementPack.SlopeTangent * config.Acceleration * dt;
minYSpeed = -config.MaxSlopeSpeed;
break;
// No movement, only deceleration
case CharacterMovementType.None:
var lerpFactor = dt * config.Braking;
if (Velocity.X.RawValue != 0) {
Velocity.X = FPMath.Lerp(Velocity.X, default, lerpFactor);
if (FPMath.Abs(Velocity.X) < FP.EN1) {
Velocity.X.RawValue = 0;
}
}
if (Velocity.Z.RawValue != 0) {
Velocity.Z = FPMath.Lerp(Velocity.Z, default, lerpFactor);
if (FPMath.Abs(Velocity.Z) < FP.EN1) {
Velocity.Z.RawValue = 0;
}
}
// we only lerp the vertical velocity back to 0 if the character is not jumping in this exact frame,
// otherwise it will jump with a lower impulse
if (Velocity.Y.RawValue != 0 && Jumped == false) {
Velocity.Y = FPMath.Lerp(Velocity.Y, default, lerpFactor);
if (FPMath.Abs(Velocity.Y) < FP.EN1) {
Velocity.Y.RawValue = 0;
}
}
minYSpeed = 0;
break;
}
// horizontal is clamped elsewhere
if (movementPack.Type != CharacterMovementType.Horizontal) {
var h = Velocity.XZ;
if (h.SqrMagnitude > MaxSpeed * MaxSpeed) {
h = h.Normalized * MaxSpeed;
}
Velocity.X = h.X;
Velocity.Y = FPMath.Clamp(Velocity.Y, minYSpeed, maxYSpeed);
Velocity.Z = h.Y;
}
// reset jump state
Jumped = false;
}
碰撞回調
每當 KCC 檢測到與碰撞器的相交時,就會觸發回調。
C#
public interface IKCCCallbacks2D
{
bool OnCharacterCollision2D(FrameBase f, EntityRef character, Physics2D.Hit hit);
void OnCharacterTrigger2D(FrameBase f, EntityRef character, Physics2D.Hit hit);
}
public interface IKCCCallbacks3D
{
bool OnCharacterCollision3D(FrameBase f, EntityRef character, Physics3D.Hit3D hit);
void OnCharacterTrigger3D(FrameBase f, EntityRef character, Physics3D.Hit3D hit);
}
要接收回調並使用其信息,請在系統中實現相應的IKCCCallbacks接口。
重要提示:請注意,碰撞回調返回一個布林值。這允許決定是否應該忽略碰撞。返回false會使角色穿過與其碰撞的物理對象。
除了實現回調外,移動方法還應傳遞IKCCCallbacks對象;下面是使用碰撞回調的代碼片段。
C#
namespace Quantum
{
using Quantum.Core;
using Quantum.Physics3D;
public unsafe class SampleSystem : SystemMainThreadFilter<SampleSystem.Filter>, IKCCCallbacks3D
{
public struct Filter
{
public EntityRef EntityRef;
public CharacterController3D* KCC;
}
public bool OnCharacterCollision3D(FrameBase f, EntityRef character, Hit3D hit)
{
// read the collision information to decide if this should or not be ignored
return true;
}
public void OnCharacterTrigger3D(FrameBase f, EntityRef character, Hit3D hit)
{
}
public override void Update(Frame frame, ref Filter filter)
{
// [...]
// adding the IKCCCallbacks3D as the last parameter (this system, in this case)
//CharacterController3D.Move(, input->Direction, this);
filter.KCC->Move(frame, filter.EntityRef, input->Direction, this);
// [...]
}
}
}