XRShared
The XRShared addon provides the base components to create a XR experience compatible with Fusion.
Purpose
The XRShare core addon provides a starting point for other XR addons.
It serves 5 purposes:
- Define a common architecture for networked XR applications,
- Provide a common framework for defining what a XR rig is and, to a lesser extent, what XR interactions are,
- Allow an XR/interaction stack to easily be packaged for this framework,
- Allow other addons to rely on the common definitions, and so to be compatible with a rig/interaction stack packaged for it,
- Provide a simple reference rig, and some basic interaction, to provide a reference implementation as well that a quickstart.
Common architecture for XR applications
In an immersive application, the rig describes all the mobile parts that are required to represent an user, usually both hands, an head, and the play area (it is the personal space that can be moved, when an user teleports for instance),
While in a networked session, every user is represented by a networked rig, whose various parts positions are synchronized over the network.
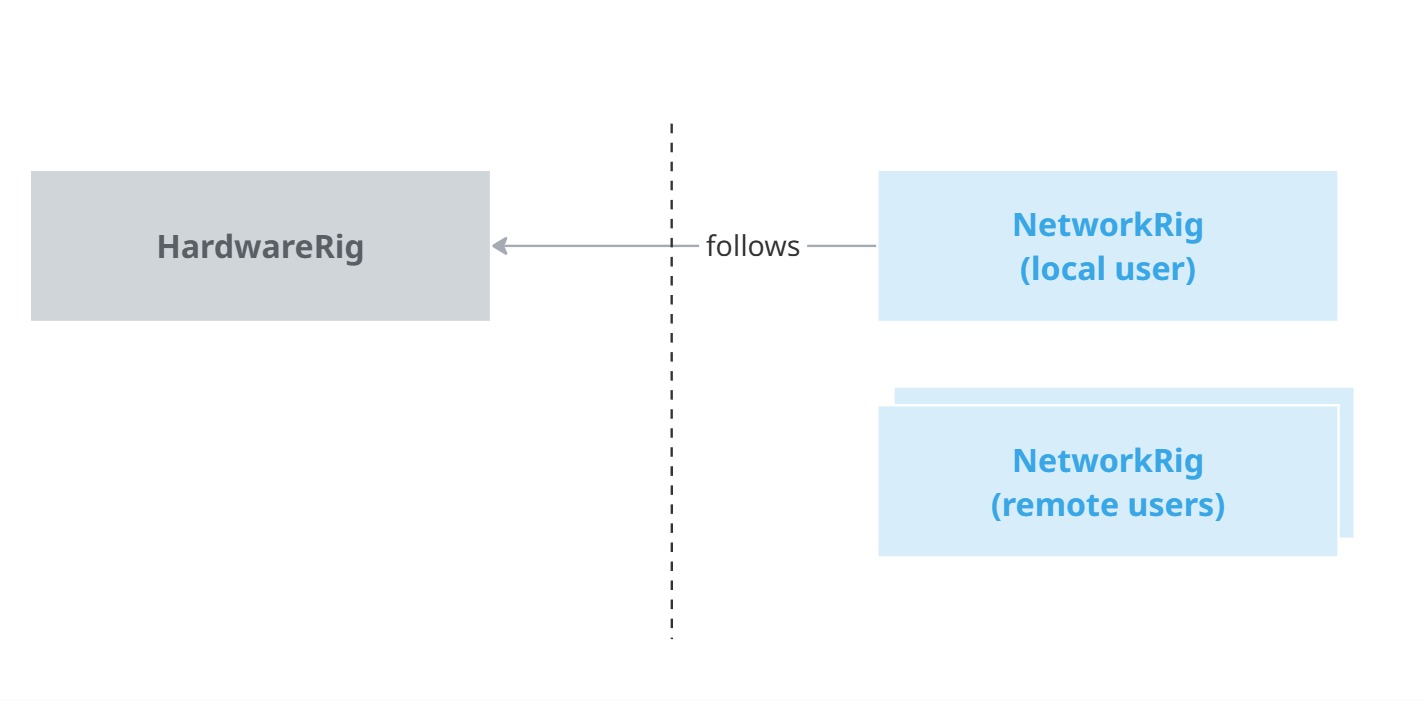
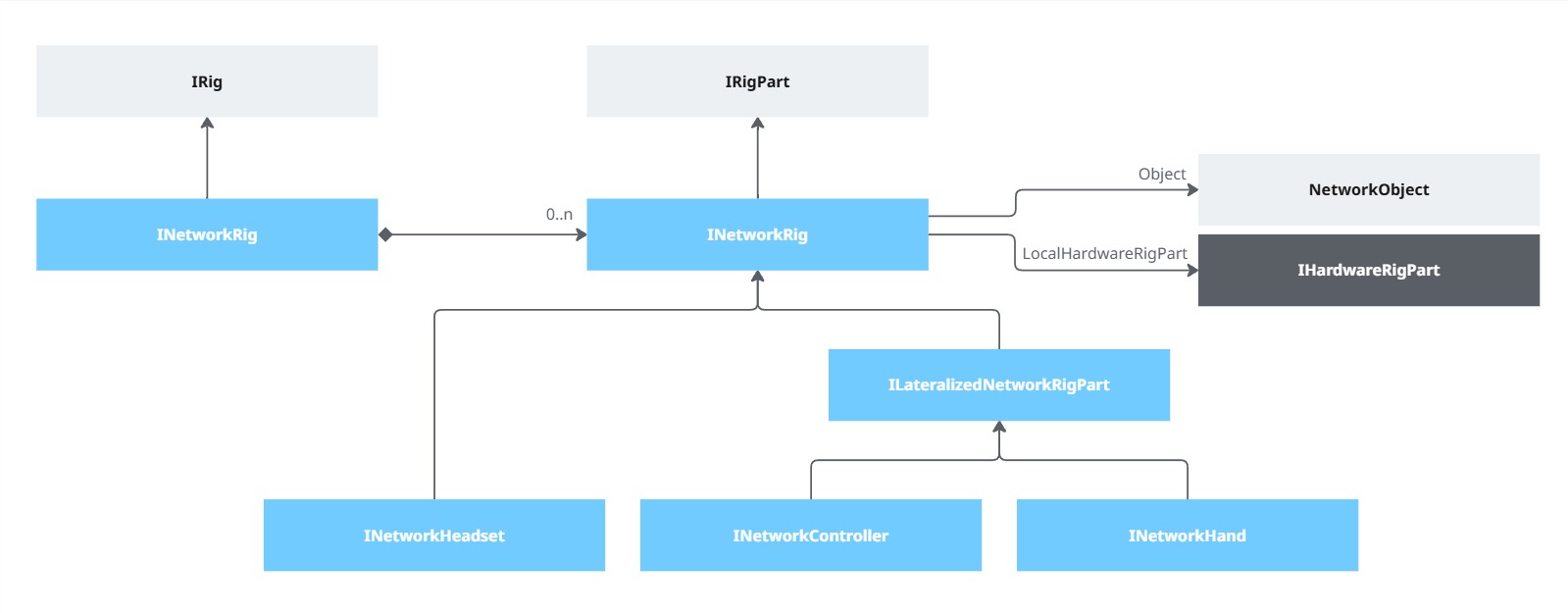
Several architectures are possible, and valid, regarding how the rig parts are organized and synchronized. Here, an user is represented by a single NetworkObject, with several nested NetworkTransforms, one for each rig parts.
Regarding the specific case of the network rig representing the local user, this rig has to be driven by the hardware inputs. To simplify this process, a separate, non networked, rig has been created, called the "Hardware rig".
It uses Unity's API to collect the hardware inputs.
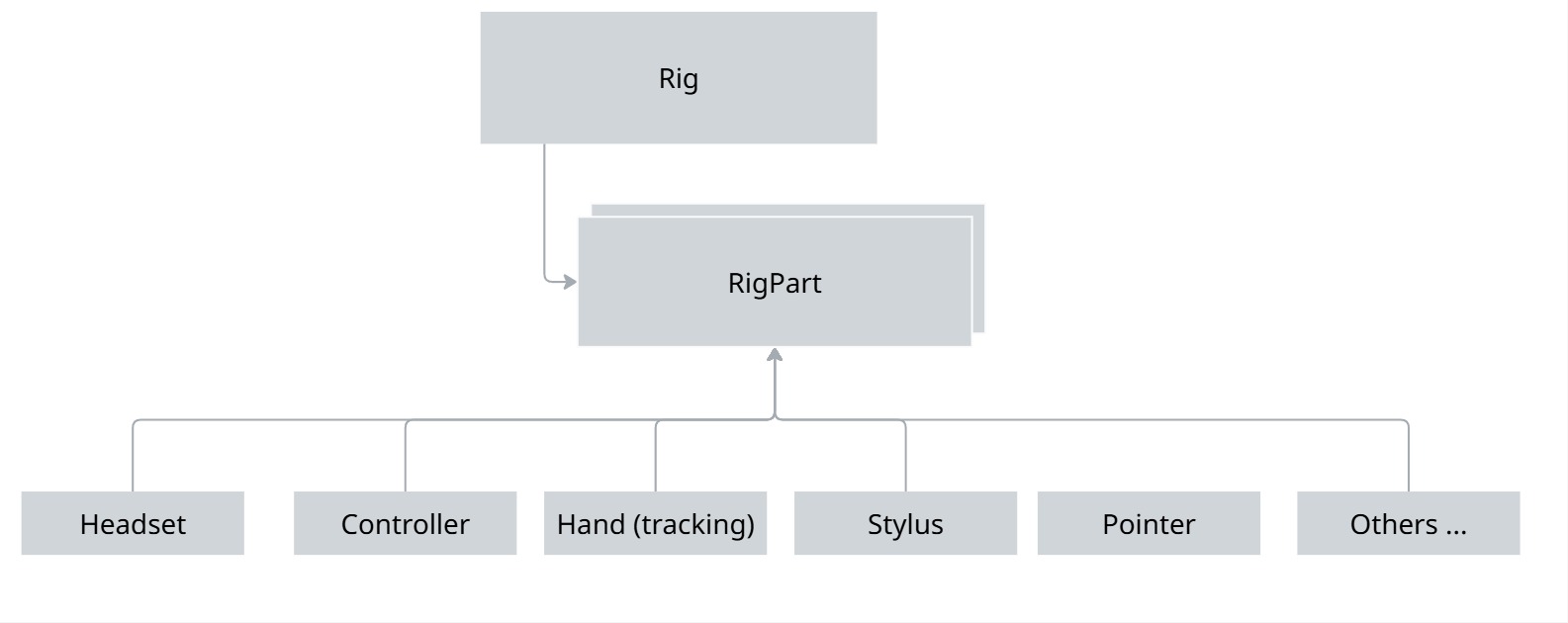
A rig part can be anything whose position needs to be tracked: a controller, the headset, a finger-tracked hand, a spatialized pen, an eye-tracking pointer, ...
Available hardware and network rigs
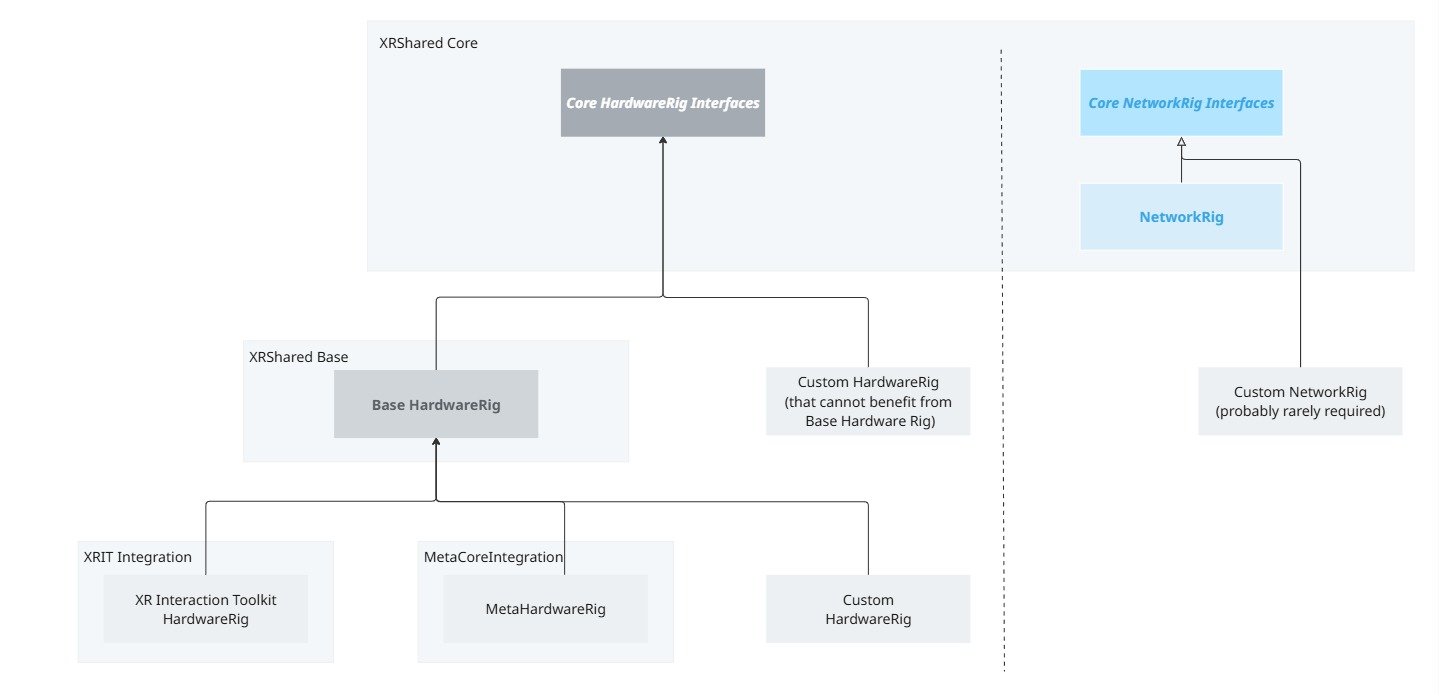
The XRShared Core module describes the basic interfaces for the hardware rig and the network rig.
Most Fusion XR addons rely on these interfaces as base constraints, so that any custom hardware or network rig implementing those interfaces could use most of the addons.
A default network rig implementation is provided, and this one should cover most needs, without requiring customization.
A default hardware rig is provided, and similarly, it should be able to serve as a base for most needs. It is the base rig for the XR Interaction toolkit addon, and the Meta core integration addon.
For any specific needs, it is possible to implement the core interfaces, or to subclass the default hardware and network rig. See customization chapter for details.
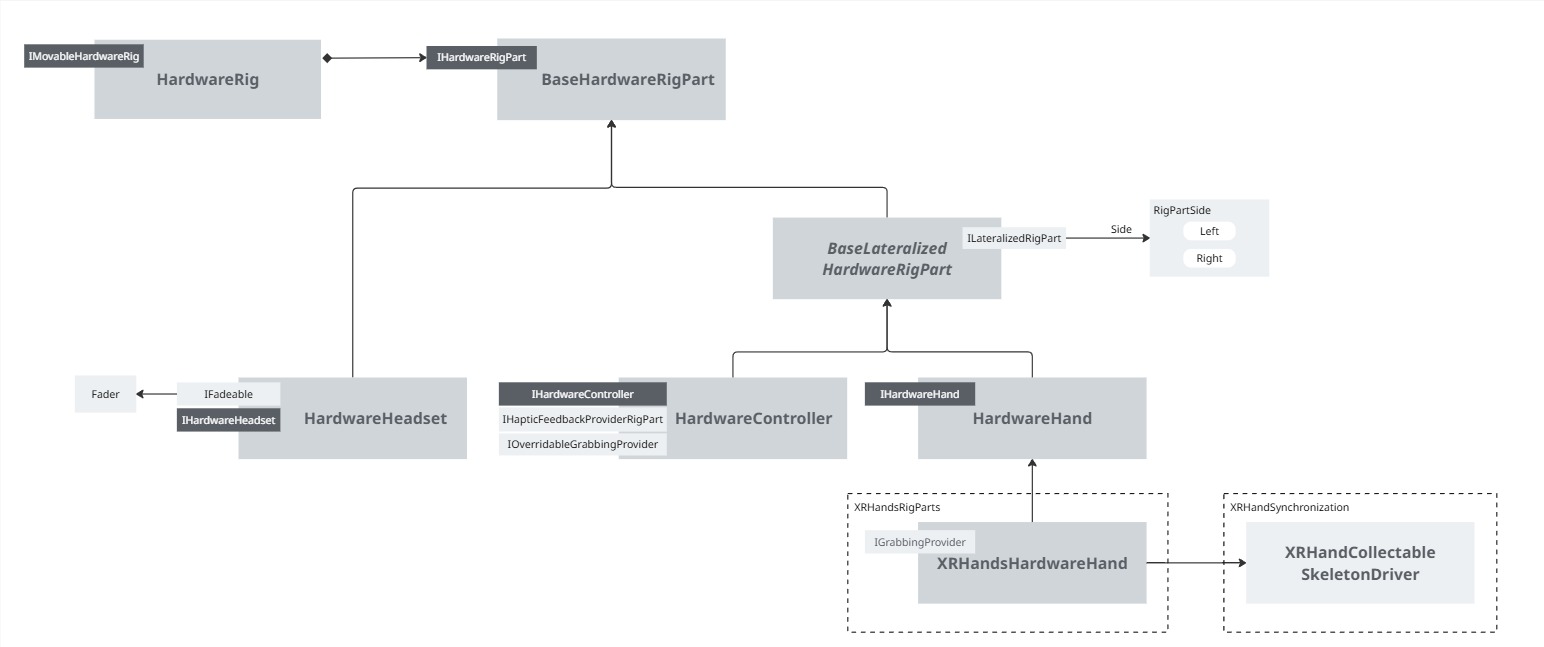
Default hardware rig
Base rig
The BaseRig module provides a default hardware rig and rig parts.
The rig and rig parts scripts allow to "tag" a game object as a rig tracking element (a controller or a headset for instance), so that their network counterpart can follow them for the local user.
Those rig parts do not handle the hardware tracking itself, they have to be used in conjunction with tracking components. You can either use components like TrackedPoseDriver, or use the InputDevice API (the XRControllerInputDevice, provided in the Core module, shows how to do so for instance).
Hand tracking
To deal with finger tracking, 2 additional modules are available:
- XRHandsSynchronization: this addon use the XRHands package to collect hand bones position on an hardware rig, and provide a network component to be placed on a network rig to synchronize efficiently the bones rotations.
You can find its own documentation on the XRHandsSynchronization addon page - XRHandsRigParts: this module simply implements a rig with the XRHandsSynchronization module
This way, the DefaultRigPrefab folder contains a HardwareRig prefab with controller and finger tracking using those scripts.
It can be used out of the box, or the rig parts and rig "tagging" scripts can be added on an existing rig (it is the approach used in the Meta Core integration addon, or the XR Interaction toolkit integration addon).
Additional features
In addition to the base of tracking the various XR components, the default rig available in BaseRig and XRHandsRigParts support additional features, such as haptic feedback, view fading, rig locomotion logic.
Those features are the implementation of some generic interfaces that could be implemented in other rig logic. See Features details and Customization for details.
Default network rig
The Core module provides a default network rig and related rig parts.
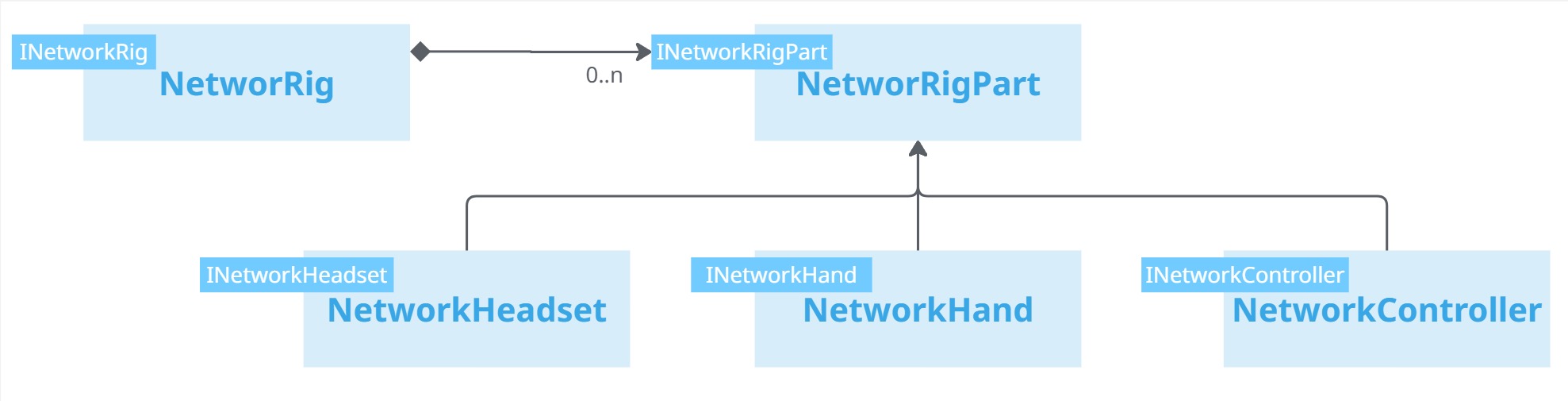
Hardware rig and rig parts detection
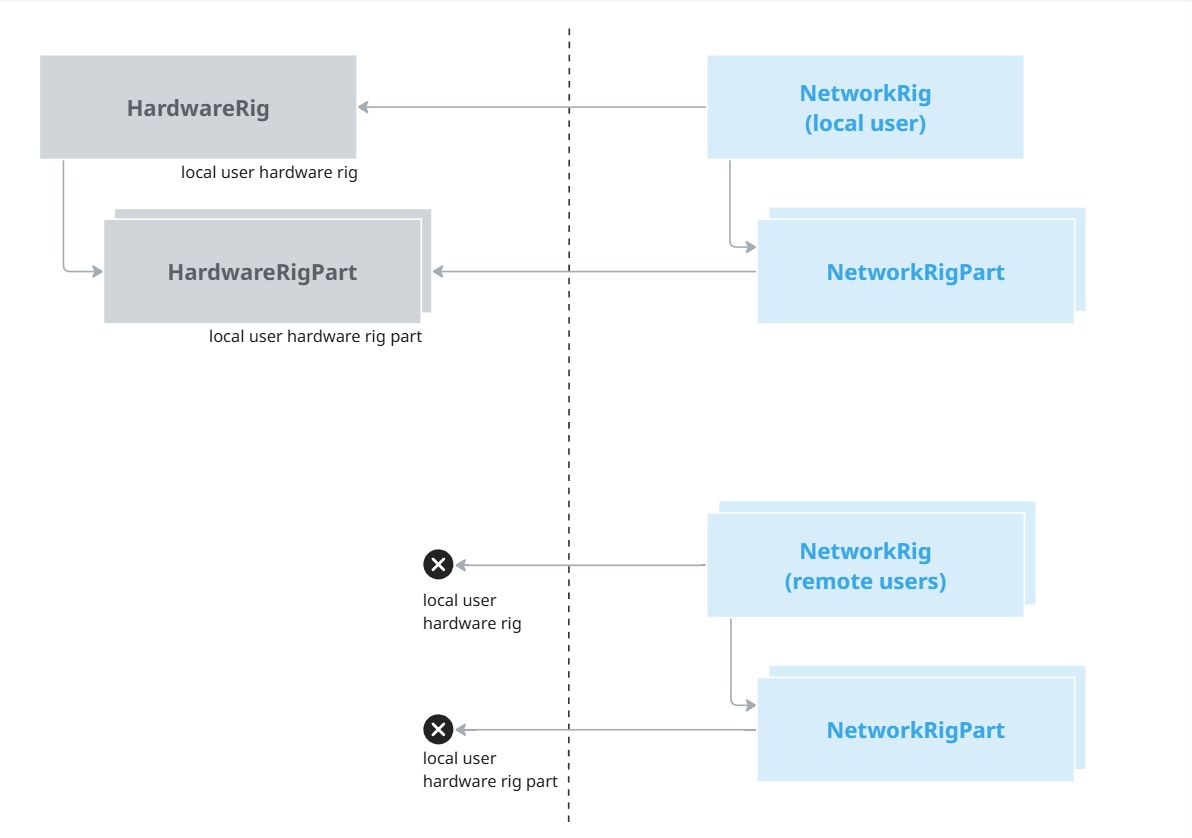
The local user hardware rig registers in a HardwareRigRegistry, so that the NetworkRig can find it.
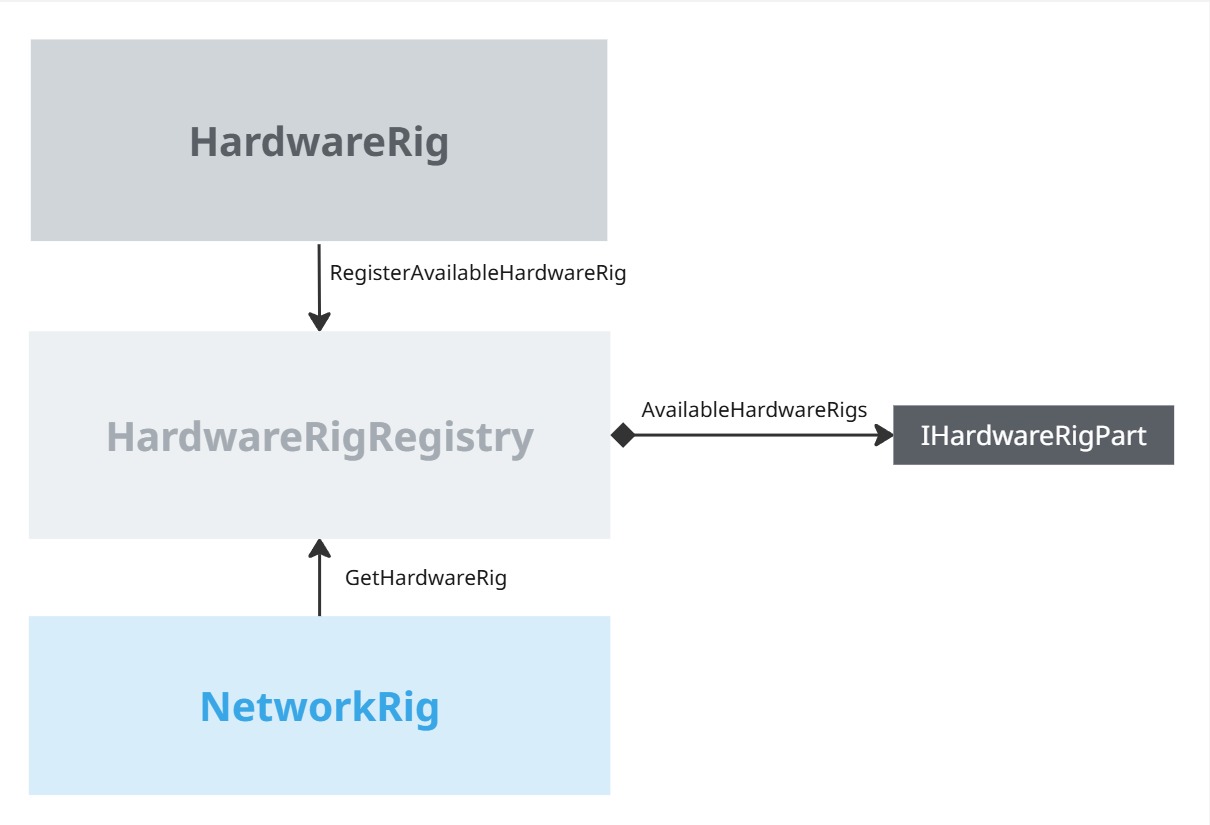
The various network rig parts then discover their matching hardware rig part in the hardware rig. The match is determined based on the kind of rig parts (headset, controller, hand, ...), and for the one with a side (hand and controllers), it is used to differentiate those lateralized components.
For more specific needs, the NetworkrigParts' IsMatchingHardwareRigPart method can be overridden to add additional criteria for other types of devices.
Network synchronization: position and tracking status
The default NetworkRigPart component ensures that the local rig part position is synchronized during Fusion's FixedUpdateNetwork. It also synchronizes the tracking status of the rig part provided by the hardware rig part.
Note that if adaptRenderersToTrackingStatus is set, the renderer display can be adapted automatically based on tracking status, by customizing the behaviour of a RigPartVisualizer. See RigPartVisualizer for details on this component.
Extrapolation for the local user
In XR, users can feel small delays, notably on their own hand moves, very easily. So for the local user rig parts, it is relevant to avoid any interpolation (displaying the positions of the object slightly in the past, to be as coherent as possible with the network state of remote objects).
To do so, we "extrapolate" during Fusion's Render the rig part's position, that is we simply read the hardware rig part position and override the position previously interpolated in the frame by positioning components like NetworkTransform.
Note that some frameworks, like XR Interaction toolkit, may update the rig parts position until pretty late in the frame. To deal with that, it is possible to require a later extrapolation on the NetworkRig component, by setting its RequiredExtrapolationTiming to DuringUnityOnBeforeRender instead of DuringFusionRender (Unity's OnBeforerender callback occurs after Fusion's Render callback).
For special capabilities (like displaying a hand blocked by an UI for instance), this extrapolation also supports position modifiers. See Position modifiers chapters for details.
Interactions
The XRShared addon provide 2 approaches for interaction synchronization:
- some generic interfaces and components, to assist in synchronizing non-networked interaction stack
- some default interaction modules working out of the box, for prototyping or simple projects
Generic interaction description
Grabbing core logic
To be able to easily provide grabbing synchronization for interactions stacks grabbing logic, the XRShared core include a basic definition of a grabbable object, through the IGrabbable interface, and a default NetworkGrabber component, to represent a rig part able to grab objects on a network rig.
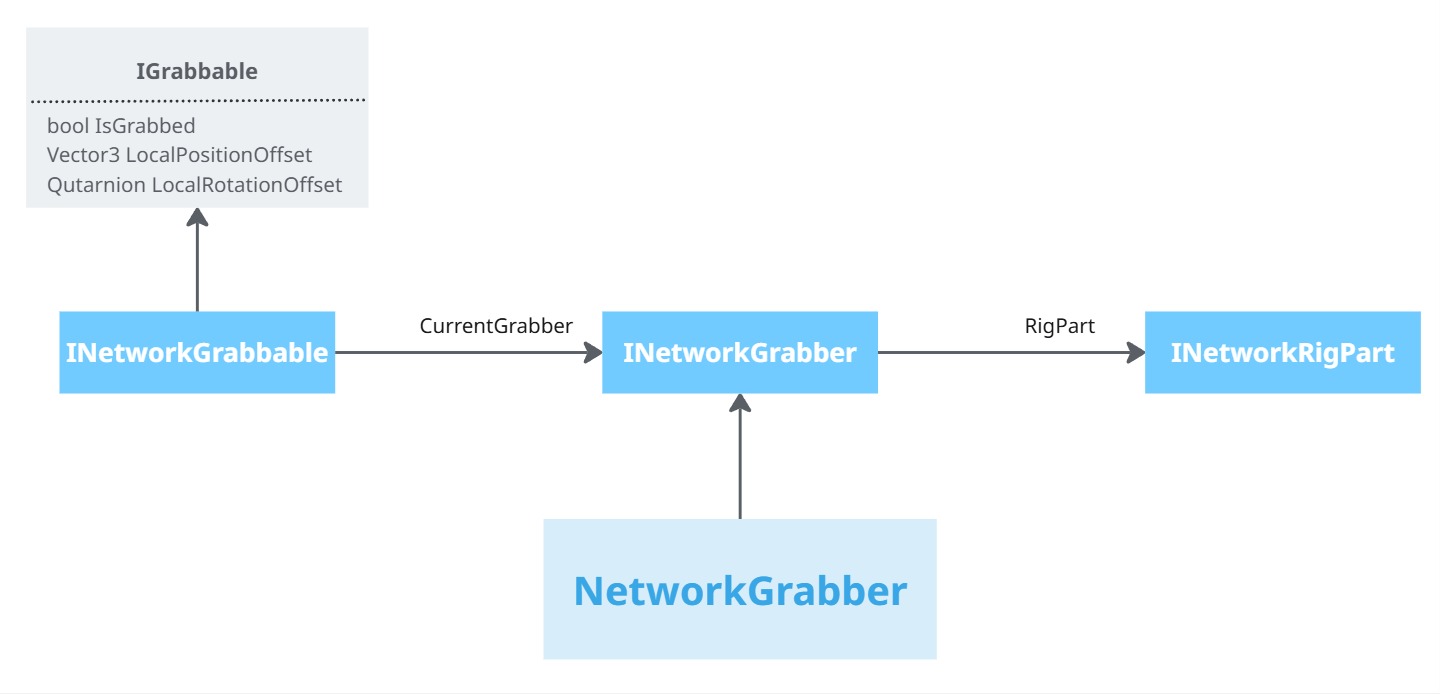
Interaction modules
The base rig described before can be used in conjunction with existing interaction stacks like Unity XR Interaction Toolkit (for instance, see XRITIntegration addon page for more details regarding this one).
For prototyping, or simple uses, the XRSharedInteraction module provides some default interaction to quick start a project.
The default rig implements some of those components, to be easily usable out of the box.
Beamer
The Beamer module provides a basic ray, that is by default triggered by pressing on any button on top of a controller. This is notably used in the UI and locomotion module, to teleport on a point aimed at.
The RayBeamer class displays a line renderer-based beam, and upon release, the RigLocomotion place next to the HardwareRig triggers the rig movement.
The RigLocomotion scripts also handles snap rotation.
Locomotion
The locomotion module provides a basic implementation to move a rig based on certain events, thus moving all rig parts.
It is mostly used to block locomotion (position validation, ...) or to react to the beamer locomotion rays.
Touch
The touch module provides the basic logic to trigger events on touching objects. It includes a TouchableButton component, that can be used for several kinf of button (press, radio or toggle button).
A generic Touchable component can be used for other object types.
See the touch hover addon for details.
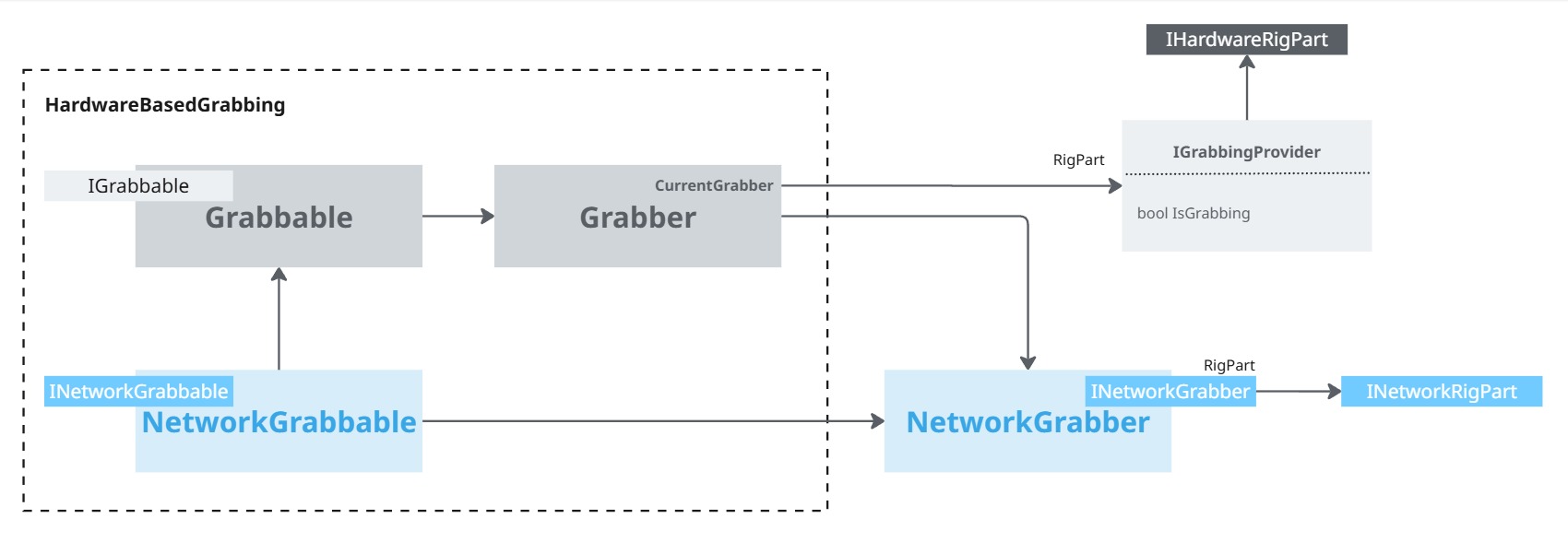
Hardware Based Grabbing
The grabbing module is called HardwareBasedGrabbing, as it relies on a grabbing system that can be used either for network synchronized objects, but also for objects interacting only with the hardware rig (for non-networked interactions, like objects moved in local menu).
It provides a Grabbable/Grabber pair of components, capable of detecting a grabber hovering a grabbable.

The grabber should be placed next to an hardware rig part, implementing the IGrabbingProvider interface to specify if it is currently triggering a grabbing or not:
- the base rig
HardwareControllerimplements this interface, grabbing when the grip button of a controller is pressed - The XRhandsRigPart's
XRHandsHardwareHandimplements this interface, grabbing when a finger pinch is detected
The networked counterpart of Grabbable , NetworkGrabbable, handles the synchronization, during FixedUpdateNetwork, of the position changes due to grabbing.
It also handles:
- Basic extrapolation: for the local user, we want to make sure the grabbable follows the hand, which may have been extrapolated to use the most up to date device information (see "Network synchronization > Extrapolation for the local user" chapter for details),
- Extrapolation while taking authority: when the state authority of the
NetworkGrabbablechanges, the incoming state authority user should see the position change locally to reflect their grabbing, even if they can't really edit theNetworkTransformposition yet.
Remote Grabbing
This kind of grabbing does not rely at all on a hardware rig to detect grabbing. It is mostly here for reference needs, and a similar logic is described in details in the VR Shared sample (it is the initial and more simple version of XRShared core)
Feature details
RigPartVisualizer
The RigPartVisualizer component can be placed next to any rig part, to adapt its renderers behaviour to the online status of the object. This way, it is for instance possible to display an hardware rig part while not online, while hiding it when online (to let the network rig part visible alone).
The RigPartVisualizer.Mode mode field allows to specify the expected behaviour for a rig part renderers.
This component can automatically detect child renderers if not specified, and an ignore list can prevent some renderers to be automatically detected.
Position modifiers
The default network rig part can accept position modifiers (IRigPartPositionModifier), placed on its local hard rig part children.
They can provide position modifiers, to slightly change the displayed position of the rig part during the Render phase. This is useful for effects like having a hand blocked by an UI while pressing on it.
UI
To use UI with the controller and hands, it is possible to insert on the scene event system a XSCInputModule, while having on the various world space canvases XSCTrackedDeviceRaycaster components (note: a TrackedDeviceRaycaster would also work, this subclass mostly ensures that the world space canvas camera is properly set).
DesktopSimulation
The architecture described here is relevant for XR application. However, it can also theoretically be used for cross-platform applications, with either XR or desktop clients.
The DesktopSimulation module provides a few components to use the provided rigs on the desktop.
This implementation, pretty simple and mostly usable in a prototyping context, is demonstrated in several addons.
Advanced reference: Custom rig creation
The default rigs (hardware and network) should cover many needs. However, most of the XR prototyping addons that are provided do not rely on those rigs explicitly, but on the underlying generic interfaces they implement.
If a custom rig is required, implementing those interfaces should ensure as much compatibility as possible with addons. Don’t hesitate to contact us for additional details regarding compatibility and required interfaces for each addon if needed.
Common rig part logic interfaces
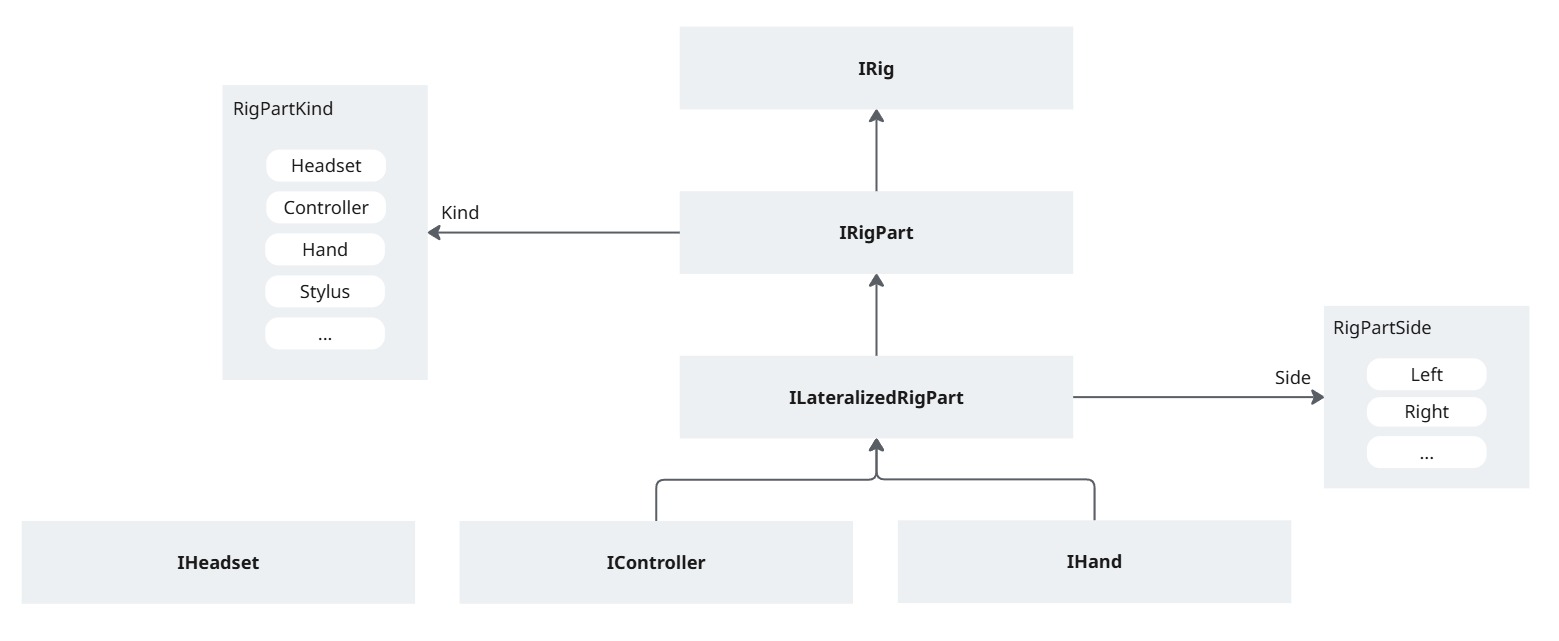
Hardware rig part interfaces
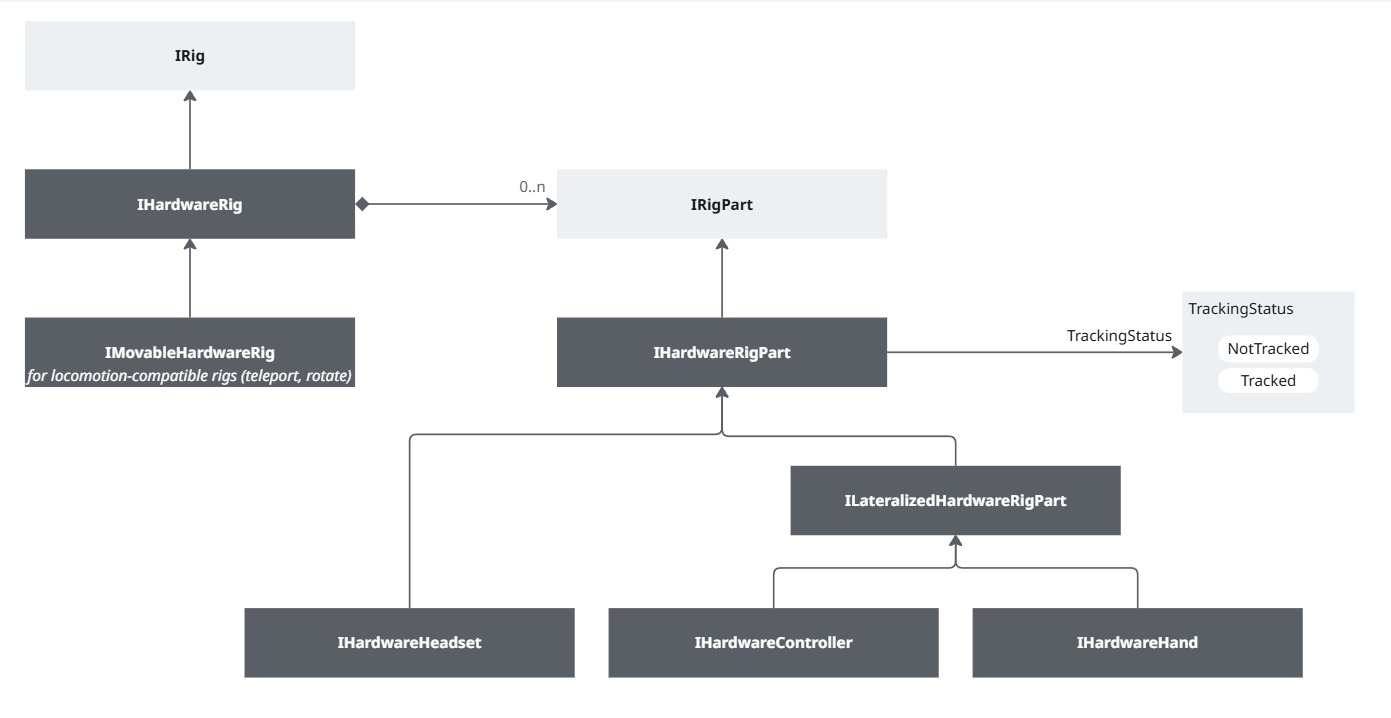
Network rig part interfaces
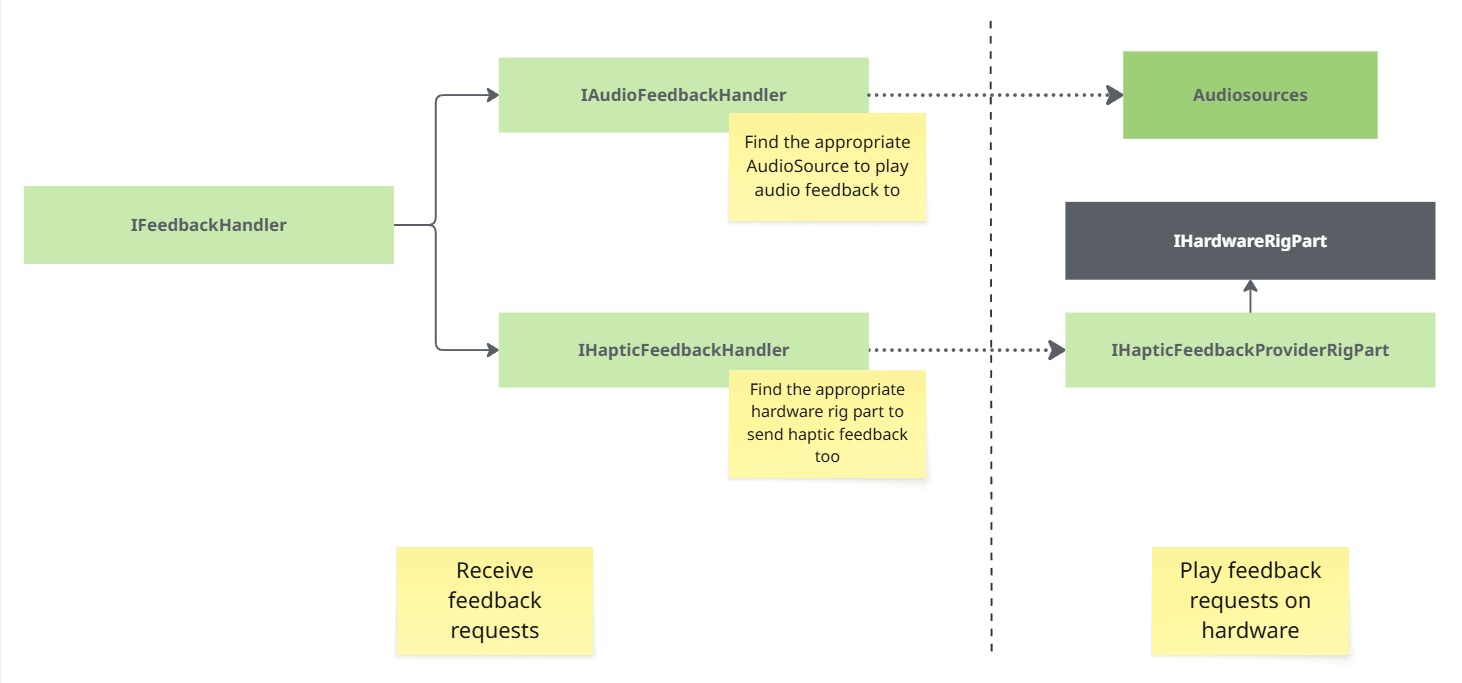
Feedback interfaces
Some components are able to request audio or haptic feedback. Those interfaces describe the rig part capable of providing haptic feedback, the component able to play audio, and so on.
Changelog
Version 2.1.11:
- Add new PermissionsRequester/PermissionWaiter permission system, to ensure that permission are not requested at the same time on Android
- Changes for Unity 6.3 Compatibility
- Fix on Grabbable.pauseGrabbability usage to work in a network context
- Add non networked visibility group handling in Visibility class
- Add TouchingSetup to add Toucher automatically to an hardware rig
- Add SimulatedHandSetup to add simulated hand to controllers in an hardware rig
Version 2.1.10:
- Add DisableForDesktop
- Add new icon in shared design
Version 2.1.9:
- Fix bug in XRHandCollectableSkeletonDriverHelper when searching for the root transform
- Add helper method to TransformManipulation to compute position offset without scale
- Add OrientedBounds to compute a bounds with an orientation
- UI interaction: fix toogle prefab (enable raycast target on images)
Version 2.1.8:
- add automatic locomotion setup options on RigLocomotion
- fix typo in IFeedbackHandler
Version 2.1.7:
- add verification on HideForLocalUser
- add material
Version 2.1.6:
- Compatibility with Fusion 2.1
- Fix for AsyncTask on WebGL
- Allow for other kind of rig part position modifiers (grabbed objects, ...)
- Add AuthorityVisualization to debug state authority visualy with a material
- Add physics grabbable and authority transfer on collision for 2.1 forecast physics
- Add new UI prefabs
Version 2.1.5: Add canvasesToIgnore option to RigPartVisualizer
Version 2.1.4: Add IColocalizationRoomProvider to add interoperability between addons in colocalization scenario
Version 2.1.3: Various assembly tooling fixes, to handle edge cases (first install, ...)
Version 2.1.2: Improve Fader shader presence in builds detection and warning message
Version 2.1.1:
- Add way to position automaticaly transforms to match wrist and index positions
- Add method in LocalInputTracker to check if a button is pressed no matter on which controller
- Fix to handle properly hardware rig detection when the build scene list is not properly configured
- Allow RigPartVisualizer to adapt game objects active status alongside changing renderers visibility
- Add RayPointer and NetworkedRayPointer to provide synchronized rays
Version 2.1.0:
- Add new locomotion system by grabbing the world
- Add new DetermineNewRigPositionToMovePositionToTargetPosition() method to TransformManipulation class
- Add some utility classes (NetworkVisibilty, RingHistory, DebugTools)
- Grabbable : add pauseGrabbabilty option
- Update & improve the automatic weaving of XR addons
- Fix TouchableButton status not reinitialized OnDisable()
- bug fixes to UI interaction (XSCInputModule)
Version 2.0.1: Add shared design & UI prefabs
Version 2.0.0: First release
- Purpose
- Common architecture for XR applications
- Available hardware and network rigs
- Default hardware rig
- Default network rig
- Hardware rig and rig parts detection
- Network synchronization: position and tracking status
- Extrapolation for the local user
- Interactions
- Feature details
- Advanced reference: Custom rig creation
- Common rig part logic interfaces
- Hardware rig part interfaces
- Network rig part interfaces
- Feedback interfaces
- Changelog